Translational, Rotational and Vibrational Energy: Difference between revisions
| (30 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
GABRIEL ALMEIDA SPRING 2022 | |||
==Main Idea== | ==Main Idea== | ||
In many cases, analyzing the kinetic energy of an object is in fact more difficult than just applying the formula <math> K = \cfrac{1}{2}mv^2 </math>. An example of this is when throwing a basketball because not only does it move through the air, but it is also rotating around its own axis. When analyzing more complicated movements like this one, it is necessary to break kinetic energy into different parts, such as rotational, translational, and vibrational, and analyze each one separately to give a more accurate picture. | In many cases, analyzing the kinetic energy of an object is in fact more difficult than just applying the formula <math> K = \cfrac{1}{2}mv^2 </math>. An example of this is when throwing a basketball because not only does it move through the air, but it is also rotating around its own axis. When analyzing more complicated movements like this one, it is necessary to break kinetic energy into different parts, such as rotational, translational, and vibrational, and analyze each one separately to give a more accurate picture. | ||
| Line 49: | Line 51: | ||
::<math>K_{rotational} =\frac{1}{2} I_{cm}{\omega}^2</math> | ::<math>K_{rotational} =\frac{1}{2} I_{cm}{\omega}^2</math> | ||
Another important rotational equation is: | |||
::<math></math> | |||
=====Moment of Inertia===== | =====Moment of Inertia===== | ||
The moment of inertia of an object shows the difficulty of rotating an object, since the larger moment of inertia the more energy required to rotate the object at the same angular velocity as an object with smaller moment of inertia. | The moment of inertia of an object shows the difficulty of rotating an object, since the larger the moment of inertia the more energy is required to rotate the object at the same angular velocity as an object with a smaller moment of inertia. The moment of inertia of an object is defined as the sum of the products of the mass of each particle in the object with the square of their distance from the axis of rotation. The general formula for calculating the moment of inertia of an object is: | ||
::<math>I = m_1{r_{1}}^2 + m_2{r_{2}}^2 + m_3{r_{3}}^2 +...</math> | |||
:::Here <math> r_1, r_2, r_3 </math> represent the perpendicular distance from the point/axis of rotation. | |||
:or | |||
<math> I = | ::<math>I = \sum_{i} m_{i}{r_{i}}^2</math> | ||
:For a body with a uniform distribution of mass this can be turned into an integral: | |||
::<math>I = \int r^2 \ dm</math> | |||
The units of rotational inertia are <math> kg \cdot m^2 </math> | |||
[[File:4c906c92cebe30d9486deb2a682acf561d23c9c1.png|900px|center]] | |||
=====Angular Speed===== | =====Angular Speed and Acceleration===== | ||
The angular speed is the rate at which the object is rotating. It is given in the following formula: | The angular speed is the rate at which the object is rotating. It is given in the following formula: | ||
[[File:Angularvelocity.png|right|200px]] | [[File:Angularvelocity.png|right|200px]] | ||
| Line 75: | Line 86: | ||
::<math>v(r)= \omega r</math> | ::<math>v(r)= \omega r</math> | ||
The angular acceleration a rotating object goes through to change its angular speed is given by: | |||
::<math>a(r) = \alpha r</math> | |||
===Computational Model=== | ===Computational Model=== | ||
: | Here is a rotating rod computational model example: | ||
https://trinket.io/glowscript/31d0f9ad9e | |||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| Line 83: | Line 100: | ||
===Simple=== | ===Simple=== | ||
A player throws a mid-court pass horizontally with a <math>624g</math> basketball. This pass covers <math>15 \ m</math> in <math>2 \ s</math>. | |||
:'''a) What is the basketball’s average translational kinetic energy while in flight? | |||
::Since the ball is moving relative to the gym, we can describe its average velocity, and thus translational kinetic energy as: | |||
:::<math>v_{avg} = \frac{d}{t} = \frac{15}{2} = 7.5 \ \frac{m}{s}</math> | |||
:::<math>K_{avg_{b}} = \frac{1}{2}m{v_{avg}}^2 = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.624 \times (7.5)^2 = 17.55 \ J</math> | |||
An average molecule of air in the basketball, has a mass of <math>29 \ u</math>, and an average speed of <math>500 \ \frac{m}{s}</math>, relative to the basketball. There are about <math>3 \times 10^{23}</math> molecules inside it, moving in random directions, when the ball is properly inflated. | |||
:'''b) What is the average translational kinetic energy of the random motion of all the molecules inside, relative to the basketball? | |||
::Since the average speed of a molecule is <math>500 \ \frac{m}{s}</math>, we can calculate the average translational kinetic energy of a given molecule: | |||
:::<math>K_{avg_{g}} = \frac{1}{2}m_{g}{v_{avg_{g}}}^2</math> | |||
::The mass of a molecule in kilograms <math>(m_{g})</math> will be the atomic mass <math>(m_{A})</math> times a conversion factor <math>(A)</math>: | |||
== | :::<math>m_{g} = m_{A}A = 29 \times 1.66 \times 10^{-27} = 4.814 \times 10^{-26} \ kg</math> | ||
::Thus, the translational kinetic energy of an average molecule relative to the ball is: | |||
:::<math>K_{avg_{g}} = \frac{1}{2}m_{g}{v_{avg_{g}}}^2 = \frac{1}{2} \times 4.814 \times 10^{-26} \times (500)^2 = 6.0175 \times 10^{-21} \ J</math> | |||
::Multiplying this kinetic energy by the number of molecules will give us our answer: | |||
:::<math>K_{avg_{total}} = N K_{avg_{g}} = 3 \times 10^{23} \times 6.0175 \times 10^{-21} = 1,805.25 \ J</math> | |||
::The kinetic energy possessed by the gas relative to the ball is <math>1,805.25</math> Joules. | |||
:'''c) How fast would the basketball have to travel relative to the court to have a kinetic energy equal to the amount in part (b)? | |||
::The basketball would have to have a translational kinetic energy equal to <math>1,805.25</math> Joules. To do this the ball's speed would have to satisfy: | |||
= | :::<math>K_{ball} = \frac{1}{2}m_{ball}v^2</math> | ||
::Solving for <math>v</math> gives: | |||
:::<math>v = \sqrt{\frac{2K_{ball}}{m_{ball}}} = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 1,805.25}{0.624}} = 76.07 \ \frac{m}{s}</math> | |||
===Middling=== | |||
== | |||
== | |||
A wheel is mounted on a stationary axel, which is nearly frictionless so that the wheel turns freely. The wheel has an inner ring with a mass of <math>5 \ kg</math> and a radius of <math>10 \ cm</math>, and an outer ring with a mass of <math>2 \ kg</math> and a radius of <math>25 \ cm</math>; the spokes have negligible mass. A string with negligible mass is wrapped around the outer ring and you pull on it, increasing the rotational speed of the wheel. | |||
:'''a) During the time that the wheel's rotation changes from 4 revolutions per second to 7 revolutions per second, how much work do you do?''' | |||
::To find the work done, the best course of action will be to find the change in kinetic energy of the wheel. To do this, we will need to find the change in angular speed and the moment of inertia of the wheel. | |||
::We are given the initial and final frequencies of rotation for the wheel: | |||
:::<math>f_{0} = 4 \ s^{-1} \quad \And \quad f_{f} = 7 \ s^{-1}</math> | |||
::The frequency of a rotation is related to its period by: | |||
:::<math>T = \frac{1}{f}</math> | |||
::Therefore, we have the initial and final period of rotation: | |||
:::<math>T_{0} = \frac{1}{f_{0}} = \frac{1}{4} = 0.25 \ s \quad \And \quad T_{f} = \frac{1}{f_{f}} = \frac{1}{7} = 0.1429 \ s</math> | |||
The | ::The period of a rotation is related to the body's angular speed by: | ||
:::<math>T = \frac{2\pi}{\omega} \quad \therefore \quad \omega = \frac{2\pi}{T}</math> | |||
::Therefore, we can calculate the initial and final angular speeds of the wheel: | |||
:::<math>\omega_{0} = \frac{2\pi}{T_{0}} = \frac{2\pi}{0.25} = 25.133 \ \left(\frac{rads}{s}\right) \quad \And \quad \omega_{f} = \frac{2\pi}{T_{f}} = \frac{2\pi}{0.1429} = 43.969 \ \left(\frac{rads}{s}\right)</math> | |||
::Now, to find the moment of inertia, we assume the separate rings are thin enough to use the moment of inertia for a thin ring, from the table above: | |||
:::<math>I = mr^2</math> | |||
::However, since there are two concentric rings that make up the wheel (ignoring the spokes), we must add their moments of inertia to calculate the total moment of inertia for the wheel: | |||
<math>1 | :::<math>I_{wheel} = I_{inner} + I_{outer} = m_{inner} r^2_{inner} + m_{outer} {r}^2_{outer} = 5 \times (0.1)^2 + 2 \times (0.25)^2 = 0.175 \ (kg \cdot m^2)</math> | ||
::Using the Energy Principle, and assuming the only work done on the wheel is due to the string being pulled, we can say: | |||
:::<math>\Delta E_{wheel} = W_{on wheel}</math> | |||
<math> | :::<math>\Delta U_{wheel} + \Delta K_{transalational_{wheel}} + \Delta K_{rotational_{wheel}} = W_{on wheel} \quad \And \quad \Delta U_{wheel} = 0 \quad \And \quad \Delta K_{translational_{wheel}} = 0</math> | ||
:::<math>\Delta K_{rotational_{wheel}} = W_{wheel}</math> | |||
::The rotational kinetic energy of the wheel is given by: | |||
:::<math>K_{rotational} = \frac{1}{2} I_{wheel} \omega_{wheel}</math> | |||
::Thus, the change in rotational kinetic energy of the wheel will be: | |||
:::<math>\Delta K_{r} = \frac{1}{2} I_{wheel} (\omega^2_{f} - \omega^2_0) = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.175 \times ((43.969)^2 - (25.133)^2) = 113.89 \ J</math> | |||
::Since we are assuming there is no friction in this process and the center of mass of the wheel does not move, all the work done is due to you pulling the string: | |||
<math> | :::<math>W_{you} = \Delta K_{r} = 113.89 \ J</math> | ||
===Difficult=== | ===Difficult=== | ||
Image: https://drive.google.com/file/d/185xWvF0iMpX-dUNc91ZOhCxQIq7-hHM3/preview | |||
a. | A common flywheel design is a flattened disk (cylinder) rotating about an axis perpendicular to its center, as shown in the figure. Let’s assume our cylinder is about a meter across ( R = 0.5 m ) and has a mass of 240 kg (i.e. has a weight of about 530 pounds). The moment of inertia for such a shape is <math> I = (1/2)MR^2 </math>. What velocity do I need the disk to rotate in order to power a house? A typical home uses energy at a rate of roughly 1000 W or 1000 J/s. | ||
<math> I = (0.5)*(240)*(0.5)^2 = 30 Kg*m^2 </math> | |||
Energy consumption in a day: | |||
<math> E{k} = 1000 * 24* 3600 = 8.64 * 10^7 J </math> | |||
<math> E = (1 / 2)Iw^2 </math> | |||
Energy = angular times inertia: | |||
<math> w = √(2E/I) </math> | |||
<math> w = √(2*8.64*10^7/30) = 2400 rad/sec </math> | |||
<math> v = r*w = 0.5 * 2400 = 1200 m/sec </math> | |||
==Connectedness== | |||
'''1. How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?''' | |||
*This topic connected to me because I used to dance when I was younger. This section focused on kinetic energy and the different parts of kinetic energy. You could break up different parts of dance and compare it to kinetic energy. | |||
*This topic resonated with my tennis experience. If you play tennis there are certain moves that generate specific rotations patterns on the ball and can either increase or decrease the length of its trajectory. Top spin, for example, involves spinning the ball forward and this leads to a positive change in K{rot} and, if we assume no change in K{trans}, an increase in K{total} that extends the ball's trajectory. | |||
'''2. How is it connected to your major?''' | |||
*In Chemical Engineering, we will focus on the kinetic energy on the microscopic level and determining the energy of the particles by looking at the translational, rotational, and vibrational energies of the atom, and how they allow chemical reactions to precess. | |||
'''3. Is there an interesting industrial application?''' | |||
*There are many machines that use kinetic energy for power, and we will probably see in a few years from now the use of rotational, translational, and vibrational energy to power anything from phones to computers. | |||
==History== | |||
Kinetic energy was first set apart from potential energy by Aristotle. Later, in the 1600's, Leibniz and Bernoulli developed the idea that <math>E \propto mv^2</math>, and they called it the 'living force.' However, it wasn't until 1829 that Gaspard-Gustave Coriolis showed the first signs of understanding kinetic energy the way that we do today by focusing on the transfer on energy in rotating water wheels. Finally, in 1849, Lord Kelvin is said to have coined the term 'kinetic energy.' | |||
==See also== | |||
===Further Reading=== | |||
*[[Point Particle Systems]]<br> | |||
*[[Real Systems]]<br> | |||
*[[Conservation of Energy]]<br> | |||
*[[Potential Energy]]<br> | |||
*[[Thermal Energy]]<br> | |||
*[[Internal Energy]]<br> | |||
*[[Center of Mass]]<br> | |||
===External Links=== | |||
*https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5qwW8WI1gkw&feature=youtu.be<br> | |||
*https://youtu.be/Cobhu3lgeMg<br> | |||
*https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=craljBk-E5g&feature=youtu.be<br> | |||
*https://youtu.be/XlFlZHfAZeE<br> | |||
*https://youtu.be/vL5yTCyRMGk<br> | |||
*https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kinetic_energy<br> | |||
*https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moment_of_inertia<br> | |||
*https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/torque-angular-momentum/torque-tutorial/a/rotational-inertia<br> | |||
*https://youtu.be/vL5yTCyRMGk | |||
==References== | |||
All problem examples, youtube videos, and images are from the websites referenced below: | |||
*http://www.robjorstad.com/Phys161/161Lab/161RotationalKinematicsSim.pdf | |||
*http://p3server.pa.msu.edu/coursewiki/doku.php?id=183_notes:energy_sep | |||
*https://cnx.org/contents/1Q9uMg_a@6.4:V7Fr-AEP@3/103-Relating-Angular-and-Trans | |||
*https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gaspard-Gustave_de_Coriolis | |||
*https://newton.ph.msstate.edu/fox/public_html/ph2213/examples10-core.pdf | |||
Latest revision as of 13:21, 18 April 2022
GABRIEL ALMEIDA SPRING 2022
Main Idea
In many cases, analyzing the kinetic energy of an object is in fact more difficult than just applying the formula [math]\displaystyle{ K = \cfrac{1}{2}mv^2 }[/math]. An example of this is when throwing a basketball because not only does it move through the air, but it is also rotating around its own axis. When analyzing more complicated movements like this one, it is necessary to break kinetic energy into different parts, such as rotational, translational, and vibrational, and analyze each one separately to give a more accurate picture.
Translational kinetic energy is the kinetic energy associated with the motion of the center of mass of an object. This would be the basketball traveling in the air from one location to another. While relative kinetic energy is the kinetic energy associated to the rotation or vibration of the atoms of the object around its center or axis. Relative kinetic energy would be the rotation of the basketball around it's axis. Later on this page, we go into more depth about the different types of kinetic energy.
Here is a link to a video which explains kinetic energy in detail: [3]
Mathematical Model
Total Kinetic Energy
As we just saw, the total kinetic energy of a multi particle system can be divided into the energy associated with motion of the center of mass and the motion relative to the center of mass.
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{total} = K_{translational} + K_{relative} }[/math]
The relative kinetic energy is composed of motion due to rotation about the center of mass and vibrations/oscillations of the object.
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{total} = K_{translational} + K_{rotational} + K_{vibrational} }[/math]
Translational Kinetic Energy
"Translation" means:
- To move from one location to another location
By calculating translational kinetic energy, we can track how one object moves from one location to another. Since the translational kinetic energy is associated with the movement of the center of mass of the object, it is important to know how to calculate the location of the center of mass and the velocity of the center of mass which is shown in the two equations below:
- [math]\displaystyle{ r_{CM} = \cfrac{m_1r_1 + m_2r_2+m_3r_3 + ...}{m_1 + m_2 +m_3} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ v_{CM} = \cfrac{m_1v_1 + m_2v_2+m_3v_3 + ...}{m_1+ m_2 +m_3} }[/math]
- Here is a link to a video if you want to refresh your knowledge on center of mass: [4]
The motion of the center of mass is described by the velocity of the center of mass. Using the total mass and the velocity of the center of mass, we define the translational kinetic energy as:
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{translational} = \cfrac{1}{2}M_{total}v_{CM}^2 }[/math]
Vibrational Kinetic Energy
The total energy due to vibrations is the sum of the potential energy associated with interactions causing the vibrations and the kinetic energy of the vibrations.
- [math]\displaystyle{ E_{vibrational} = K_{vibrational} + U_{s} }[/math]
The easiest way to find vibrational kinetic energy is by knowing the other energy terms and isolating the vibrational kinetic energy. This is when there is no rotational kinetic energy:
- [math]\displaystyle{ E_{total} = K_{trans} + K_{vibrational} + U_{s} +E_{rest} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{vibrational} = E_{total} - (K_{trans} + U_{s} +E_{rest}) }[/math]
Rotational Kinetic Energy
Rotational kinetic energy is the energy due to the rotation about the center of mass. It can be calculated by finding the angular momentum and inertia of the system, which will be discussed in greater detail in the next two sections. The equation used to find kinetic rotational energy is below:
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{rotational} =\frac{1}{2} I_{cm}{\omega}^2 }[/math]
Another important rotational equation is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ }[/math]
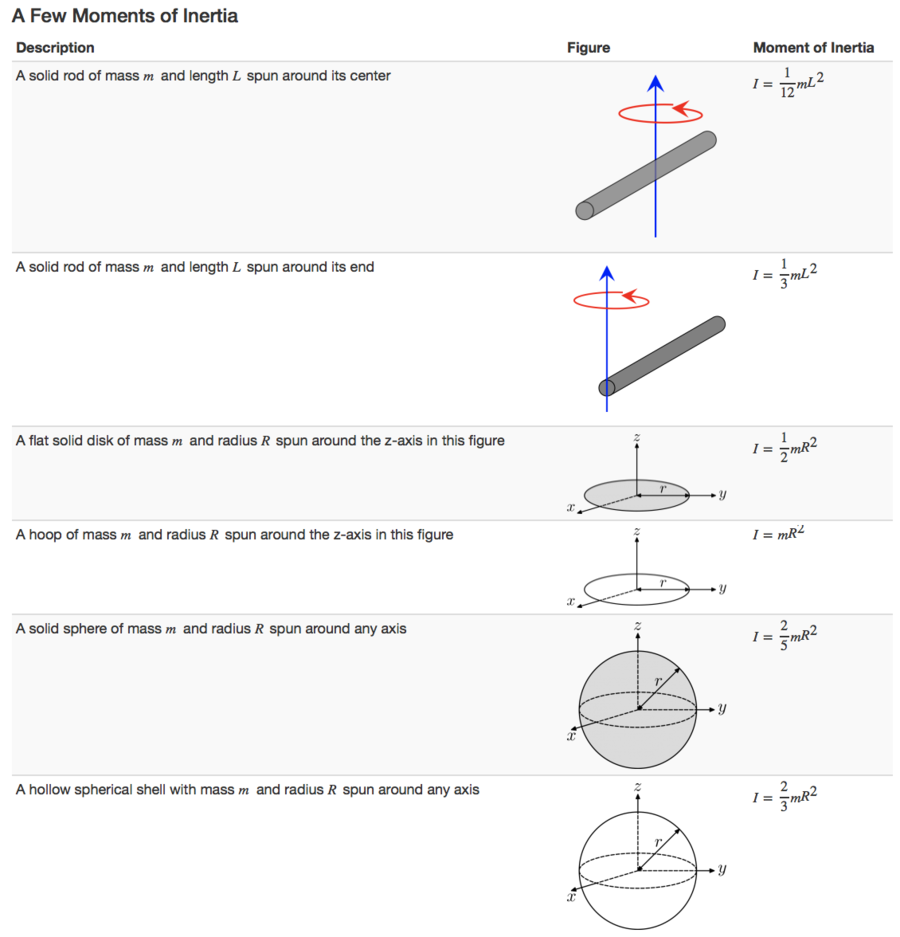
Moment of Inertia
The moment of inertia of an object shows the difficulty of rotating an object, since the larger the moment of inertia the more energy is required to rotate the object at the same angular velocity as an object with a smaller moment of inertia. The moment of inertia of an object is defined as the sum of the products of the mass of each particle in the object with the square of their distance from the axis of rotation. The general formula for calculating the moment of inertia of an object is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ I = m_1{r_{1}}^2 + m_2{r_{2}}^2 + m_3{r_{3}}^2 +... }[/math]
- Here [math]\displaystyle{ r_1, r_2, r_3 }[/math] represent the perpendicular distance from the point/axis of rotation.
- or
- [math]\displaystyle{ I = \sum_{i} m_{i}{r_{i}}^2 }[/math]
- For a body with a uniform distribution of mass this can be turned into an integral:
- [math]\displaystyle{ I = \int r^2 \ dm }[/math]
The units of rotational inertia are [math]\displaystyle{ kg \cdot m^2 }[/math]
Angular Speed and Acceleration
The angular speed is the rate at which the object is rotating. It is given in the following formula:
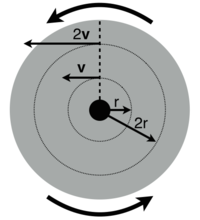
- [math]\displaystyle{ \omega = \cfrac{2\pi}{T} }[/math], where
- [math]\displaystyle{ T = }[/math] the period of the rotation
The angle in which a disk turns is [math]\displaystyle{ 2 \pi }[/math] in a time [math]\displaystyle{ T }[/math]. It is measured in radians per second. The tangential velocity of an object is related to its radius r at the angular speed because the tangential velocity increases when the distance from the center of an object increases. It is shown in the equation below:
- [math]\displaystyle{ v(r)= \omega r }[/math]
The angular acceleration a rotating object goes through to change its angular speed is given by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ a(r) = \alpha r }[/math]
Computational Model
Here is a rotating rod computational model example:
https://trinket.io/glowscript/31d0f9ad9e
Examples
Simple
A player throws a mid-court pass horizontally with a [math]\displaystyle{ 624g }[/math] basketball. This pass covers [math]\displaystyle{ 15 \ m }[/math] in [math]\displaystyle{ 2 \ s }[/math].
- a) What is the basketball’s average translational kinetic energy while in flight?
- Since the ball is moving relative to the gym, we can describe its average velocity, and thus translational kinetic energy as:
- [math]\displaystyle{ v_{avg} = \frac{d}{t} = \frac{15}{2} = 7.5 \ \frac{m}{s} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{avg_{b}} = \frac{1}{2}m{v_{avg}}^2 = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.624 \times (7.5)^2 = 17.55 \ J }[/math]
An average molecule of air in the basketball, has a mass of [math]\displaystyle{ 29 \ u }[/math], and an average speed of [math]\displaystyle{ 500 \ \frac{m}{s} }[/math], relative to the basketball. There are about [math]\displaystyle{ 3 \times 10^{23} }[/math] molecules inside it, moving in random directions, when the ball is properly inflated.
- b) What is the average translational kinetic energy of the random motion of all the molecules inside, relative to the basketball?
- Since the average speed of a molecule is [math]\displaystyle{ 500 \ \frac{m}{s} }[/math], we can calculate the average translational kinetic energy of a given molecule:
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{avg_{g}} = \frac{1}{2}m_{g}{v_{avg_{g}}}^2 }[/math]
- The mass of a molecule in kilograms [math]\displaystyle{ (m_{g}) }[/math] will be the atomic mass [math]\displaystyle{ (m_{A}) }[/math] times a conversion factor [math]\displaystyle{ (A) }[/math]:
- [math]\displaystyle{ m_{g} = m_{A}A = 29 \times 1.66 \times 10^{-27} = 4.814 \times 10^{-26} \ kg }[/math]
- Thus, the translational kinetic energy of an average molecule relative to the ball is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{avg_{g}} = \frac{1}{2}m_{g}{v_{avg_{g}}}^2 = \frac{1}{2} \times 4.814 \times 10^{-26} \times (500)^2 = 6.0175 \times 10^{-21} \ J }[/math]
- Multiplying this kinetic energy by the number of molecules will give us our answer:
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{avg_{total}} = N K_{avg_{g}} = 3 \times 10^{23} \times 6.0175 \times 10^{-21} = 1,805.25 \ J }[/math]
- The kinetic energy possessed by the gas relative to the ball is [math]\displaystyle{ 1,805.25 }[/math] Joules.
- c) How fast would the basketball have to travel relative to the court to have a kinetic energy equal to the amount in part (b)?
- The basketball would have to have a translational kinetic energy equal to [math]\displaystyle{ 1,805.25 }[/math] Joules. To do this the ball's speed would have to satisfy:
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{ball} = \frac{1}{2}m_{ball}v^2 }[/math]
- Solving for [math]\displaystyle{ v }[/math] gives:
- [math]\displaystyle{ v = \sqrt{\frac{2K_{ball}}{m_{ball}}} = \sqrt{\frac{2 \times 1,805.25}{0.624}} = 76.07 \ \frac{m}{s} }[/math]
Middling
A wheel is mounted on a stationary axel, which is nearly frictionless so that the wheel turns freely. The wheel has an inner ring with a mass of [math]\displaystyle{ 5 \ kg }[/math] and a radius of [math]\displaystyle{ 10 \ cm }[/math], and an outer ring with a mass of [math]\displaystyle{ 2 \ kg }[/math] and a radius of [math]\displaystyle{ 25 \ cm }[/math]; the spokes have negligible mass. A string with negligible mass is wrapped around the outer ring and you pull on it, increasing the rotational speed of the wheel.
- a) During the time that the wheel's rotation changes from 4 revolutions per second to 7 revolutions per second, how much work do you do?
- To find the work done, the best course of action will be to find the change in kinetic energy of the wheel. To do this, we will need to find the change in angular speed and the moment of inertia of the wheel.
- We are given the initial and final frequencies of rotation for the wheel:
- [math]\displaystyle{ f_{0} = 4 \ s^{-1} \quad \And \quad f_{f} = 7 \ s^{-1} }[/math]
- The frequency of a rotation is related to its period by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ T = \frac{1}{f} }[/math]
- Therefore, we have the initial and final period of rotation:
- [math]\displaystyle{ T_{0} = \frac{1}{f_{0}} = \frac{1}{4} = 0.25 \ s \quad \And \quad T_{f} = \frac{1}{f_{f}} = \frac{1}{7} = 0.1429 \ s }[/math]
- The period of a rotation is related to the body's angular speed by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ T = \frac{2\pi}{\omega} \quad \therefore \quad \omega = \frac{2\pi}{T} }[/math]
- Therefore, we can calculate the initial and final angular speeds of the wheel:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \omega_{0} = \frac{2\pi}{T_{0}} = \frac{2\pi}{0.25} = 25.133 \ \left(\frac{rads}{s}\right) \quad \And \quad \omega_{f} = \frac{2\pi}{T_{f}} = \frac{2\pi}{0.1429} = 43.969 \ \left(\frac{rads}{s}\right) }[/math]
- Now, to find the moment of inertia, we assume the separate rings are thin enough to use the moment of inertia for a thin ring, from the table above:
- [math]\displaystyle{ I = mr^2 }[/math]
- However, since there are two concentric rings that make up the wheel (ignoring the spokes), we must add their moments of inertia to calculate the total moment of inertia for the wheel:
- [math]\displaystyle{ I_{wheel} = I_{inner} + I_{outer} = m_{inner} r^2_{inner} + m_{outer} {r}^2_{outer} = 5 \times (0.1)^2 + 2 \times (0.25)^2 = 0.175 \ (kg \cdot m^2) }[/math]
- Using the Energy Principle, and assuming the only work done on the wheel is due to the string being pulled, we can say:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta E_{wheel} = W_{on wheel} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta U_{wheel} + \Delta K_{transalational_{wheel}} + \Delta K_{rotational_{wheel}} = W_{on wheel} \quad \And \quad \Delta U_{wheel} = 0 \quad \And \quad \Delta K_{translational_{wheel}} = 0 }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta K_{rotational_{wheel}} = W_{wheel} }[/math]
- The rotational kinetic energy of the wheel is given by:
- [math]\displaystyle{ K_{rotational} = \frac{1}{2} I_{wheel} \omega_{wheel} }[/math]
- Thus, the change in rotational kinetic energy of the wheel will be:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta K_{r} = \frac{1}{2} I_{wheel} (\omega^2_{f} - \omega^2_0) = \frac{1}{2} \times 0.175 \times ((43.969)^2 - (25.133)^2) = 113.89 \ J }[/math]
- Since we are assuming there is no friction in this process and the center of mass of the wheel does not move, all the work done is due to you pulling the string:
- [math]\displaystyle{ W_{you} = \Delta K_{r} = 113.89 \ J }[/math]
Difficult
Image: https://drive.google.com/file/d/185xWvF0iMpX-dUNc91ZOhCxQIq7-hHM3/preview
A common flywheel design is a flattened disk (cylinder) rotating about an axis perpendicular to its center, as shown in the figure. Let’s assume our cylinder is about a meter across ( R = 0.5 m ) and has a mass of 240 kg (i.e. has a weight of about 530 pounds). The moment of inertia for such a shape is [math]\displaystyle{ I = (1/2)MR^2 }[/math]. What velocity do I need the disk to rotate in order to power a house? A typical home uses energy at a rate of roughly 1000 W or 1000 J/s.
[math]\displaystyle{ I = (0.5)*(240)*(0.5)^2 = 30 Kg*m^2 }[/math]
Energy consumption in a day:
[math]\displaystyle{ E{k} = 1000 * 24* 3600 = 8.64 * 10^7 J }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ E = (1 / 2)Iw^2 }[/math]
Energy = angular times inertia:
[math]\displaystyle{ w = √(2E/I) }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ w = √(2*8.64*10^7/30) = 2400 rad/sec }[/math] [math]\displaystyle{ v = r*w = 0.5 * 2400 = 1200 m/sec }[/math]
Connectedness
1. How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- This topic connected to me because I used to dance when I was younger. This section focused on kinetic energy and the different parts of kinetic energy. You could break up different parts of dance and compare it to kinetic energy.
- This topic resonated with my tennis experience. If you play tennis there are certain moves that generate specific rotations patterns on the ball and can either increase or decrease the length of its trajectory. Top spin, for example, involves spinning the ball forward and this leads to a positive change in K{rot} and, if we assume no change in K{trans}, an increase in K{total} that extends the ball's trajectory.
2. How is it connected to your major?
- In Chemical Engineering, we will focus on the kinetic energy on the microscopic level and determining the energy of the particles by looking at the translational, rotational, and vibrational energies of the atom, and how they allow chemical reactions to precess.
3. Is there an interesting industrial application?
- There are many machines that use kinetic energy for power, and we will probably see in a few years from now the use of rotational, translational, and vibrational energy to power anything from phones to computers.
History
Kinetic energy was first set apart from potential energy by Aristotle. Later, in the 1600's, Leibniz and Bernoulli developed the idea that [math]\displaystyle{ E \propto mv^2 }[/math], and they called it the 'living force.' However, it wasn't until 1829 that Gaspard-Gustave Coriolis showed the first signs of understanding kinetic energy the way that we do today by focusing on the transfer on energy in rotating water wheels. Finally, in 1849, Lord Kelvin is said to have coined the term 'kinetic energy.'
See also
Further Reading
- Point Particle Systems
- Real Systems
- Conservation of Energy
- Potential Energy
- Thermal Energy
- Internal Energy
- Center of Mass
External Links
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5qwW8WI1gkw&feature=youtu.be
- https://youtu.be/Cobhu3lgeMg
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=craljBk-E5g&feature=youtu.be
- https://youtu.be/XlFlZHfAZeE
- https://youtu.be/vL5yTCyRMGk
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kinetic_energy
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moment_of_inertia
- https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/torque-angular-momentum/torque-tutorial/a/rotational-inertia
- https://youtu.be/vL5yTCyRMGk
References
All problem examples, youtube videos, and images are from the websites referenced below: