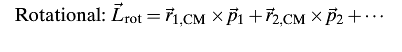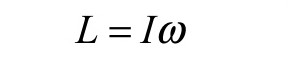Rotational Angular Momentum
Main Idea
Angular momentum is a measure of rotational momentum, and total angular momentum can be defined as the sum of translational angular momentum and rotational angular momentum. This page covers rotational angular momentum or the angular momentum relative to a center of mass. More specifically, rotational angular momentum can be defined as components of a system that rotate all around its center of mass with the same angular velocity, and it can be used to demonstrate motion such as Earth's revolution.
Mathematical Model
There are two equations that can be used to describe rotational angular momentum. The first one is a generalized form that can be described as the sum of cross products of distance and momentum.
The next equation summarizes rotational angular momentum as the product of inertia and angular velocity. (The units of rotational angular momentum are kg*m^2/s.
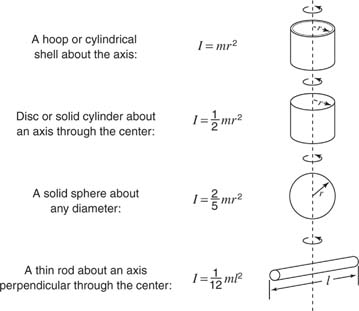
To use the above equation, the following equations may be needed. The first equation is used to calculate inertia. Inertia can be defined as the tendency to resist changes in their state of motion. (The units of inertia are kg*m^2.)
The next equation angular velocity which is the rate of change of angular position of a rotating object. (The units of angular velocity are radians per second).
A Computational Model
How do we visualize or predict using this topic. Consider embedding some vpython code here Teach hands-on with GlowScript
Examples
Listed below are examples of rotational angular momentum problems.
Simple
This is an example of a straightforward problem of rotational angular momentum.

Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page
First Law
The first law of thermodynamics defines the internal energy (E) as equal to the difference between heat transfer (Q) into a system and work (W) done by the system. Heat removed from a system would be given a negative sign and heat applied to the system would be given a positive sign. Internal energy can be converted into other types of energy because it acts like potential energy. Heat and work, however, cannot be stored or conserved independently because they depend on the process. This allows for many different possible states of a system to exist. There can be a process known as the adiabatic process in which there is no heat transfer. This occurs when a system is full insulated from the outside environment. The implementation of this law also brings about another useful state variable, enthalpy.
A Mathematical Model
E2 - E1 = Q - W
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Middling
Difficult
Connectedness
- How is this topic connected to something that you are interested in?
- How is it connected to your major?
- Is there an interesting industrial application?
History
Put this idea in historical context. Give the reader the Who, What, When, Where, and Why.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
Internet resources on this topic
References
https://www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/thermo0.html http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/thermo/thereq.html