Bohr Model: Difference between revisions
Pearlruparel (talk | contribs) (Created page with "by Pearl Ruparel") |
Pearlruparel (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
by Pearl Ruparel | by Pearl Ruparel | ||
==Main Idea== | |||
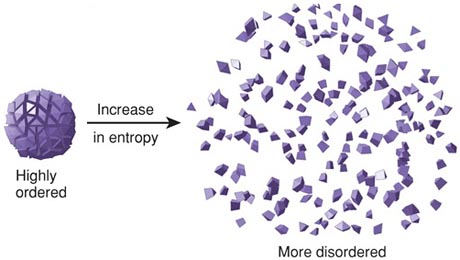
Thermodynamics is a huge area of physics that deals with study of effects of work, heat, and energy on a system. It is concerned with large scale observations. There is zeroth law, first law, and second law of thermodynamics. The zeroth law involves simple definition of thermodynamic equilibrium while the first law deals mainly with kinetic and potential energy and transfer of heat and internal energy while introducing enthalpy which leads to second law of thermodynamics. The second law of thermodynamics stipulates that the total entropy of a system plus its environment can not decrease; it can remain constant for a reversible process but must always increase for an irreversible process. Entropy is described as measure of disorder in a closed system/ thermal energy not available to do work. | |||
[[File:entropy1.jpg]] | |||
===A Mathematical Model=== | |||
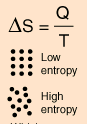
Entropy is a state variable whose change is defined for a reversible process at T where Q is the heat absorbed. It can be calculated for a reaction using the equation \deltaS = Q / T where Q is the heat absorbed for temperature T. | |||
[[File:Screen_Shot_2015-11-30_at_2.50.57_PM.png ]] | |||
===A Computational Model=== | |||
How do we visualize or predict using this topic. Consider embedding some vpython code here [https://trinket.io/glowscript/31d0f9ad9e Teach hands-on with GlowScript] | |||
Revision as of 12:45, 1 December 2015
by Pearl Ruparel
Main Idea
Thermodynamics is a huge area of physics that deals with study of effects of work, heat, and energy on a system. It is concerned with large scale observations. There is zeroth law, first law, and second law of thermodynamics. The zeroth law involves simple definition of thermodynamic equilibrium while the first law deals mainly with kinetic and potential energy and transfer of heat and internal energy while introducing enthalpy which leads to second law of thermodynamics. The second law of thermodynamics stipulates that the total entropy of a system plus its environment can not decrease; it can remain constant for a reversible process but must always increase for an irreversible process. Entropy is described as measure of disorder in a closed system/ thermal energy not available to do work.
A Mathematical Model
Entropy is a state variable whose change is defined for a reversible process at T where Q is the heat absorbed. It can be calculated for a reaction using the equation \deltaS = Q / T where Q is the heat absorbed for temperature T.
A Computational Model
How do we visualize or predict using this topic. Consider embedding some vpython code here Teach hands-on with GlowScript