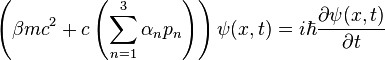Paul Dirac
jbuehler3
Born in August 1902, Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac was an influential theoretical physicist. Throughout his life he worked on quantum mechanics and even invented a new subfield of quantum electrodynamics. He won a Nobel Prize in 1933. He had a family with a wife, two of his own children, and two adopted children. He died in 1984.
The Main Idea
Dirac's work in theoretical physics was monumental in the creation and modernization of quantum physics. He derived equations that are critical in in applying the relativistic model of space time into quantum mechanics. While working alongside many famous and influential physicists of his time including Einstien, Shrodinger, and Feynman, he helped to tie many other equations and natural phenomenon together into mathmatics. He was once quoted saying that the laws of nature should be described by beautiful equations.
A Mathematical Model
The Dirac equation is a combination many discoveries and innovations that were occurring at the beginning of the 20th century. The equation helps to relate the wave function of an electron to the curvature of spacetime. In order to do this, both the Planck constant(h) and the Shrodinger equation are referenced.
The second form of the equation helps to make the math fit with Pauli matrices. This added dimension allows the algebra to work for a pseudo orthoganal 4D space, which is necessary to consider the application of momentum on a curved spacetime.
In order to continue simplification, the equation becomes
which replaced the Planck constant and the speed of light with 1 which is often called natural units. This form of the equation still creates the same model of space.
These equations were monumental in the discovery of antimatter and the positron. They are unique in the fact that they reconcile general relativity with quantum mechanics.
History
Dirac was from Bristol, England and he was born on 8 August, 1902. He was a Swiss national until he was naturalized. He attended the University of Bristol and the University of Cambridge, both on scholarship. He did research in the field of quantum electrodynamics and quantum physics for the years to come. Some said that he was obsessed and weird. In 1933 he shared a Nobel Prize with Erwin Schrodinger for the development of new models and equations for atoms. When he was 35 he married Margit Wigner, and adopted both of her children. The couple later went on to have two more children of their own. He continued to write papers, do research, and teach for the rest of his life. He moved to America to be closer to his daughter. He died at the age of 82 in Tallahassee, Florida.
Connectedness
Although we did not go into much depth on any kind of quantum physics, these equations are still fundamental to understanding the current relativistic and quantum models of the universe. Physics one concentrates much more on the macro side of molecules and systems.
These models do not really have any practical industrial use because they are mainly theoretical. While Dirac was trying to explain how the universe worked, he was not as much focused on how to apply that to industry.
Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering does not focus on the deep math that makes up much of quantum physics because it is not very applicable to the job field.
See also
http://www.physicsbook.gatech.edu/Erwin_Schrodinger http://www.physicsbook.gatech.edu/Albert_Einstein http://www.physicsbook.gatech.edu/Max_Planck http://www.physicsbook.gatech.edu/Electromagnetic_Propagation
Further reading
http://www-history.mcs.st-and.ac.uk/Biographies/Dirac.html http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1933/dirac-bio.html https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Paul_Dirac https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dirac_equation
References
http://www.nyu.edu/classes/tuckerman/quant.mech/lectures/lecture_6/node5.html http://www.britannica.com/biography/Paul-Dirac http://www.famousscientists.org/paul-dirac/