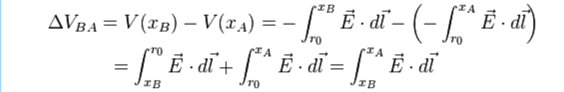Electric Potential Difference: Difference between revisions
Dkurniawan3 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Dkurniawan3 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
'''Definition''' | '''Definition''' | ||
Say you have two points " | Say you have two points "A" and "B" in space. The potential difference is defined as the difference in electric potential between those two points. Electric potential is electric potential energy per unit charge, measured in joules per coulomb, otherwise known as volts. | ||
'''Calculating Potential Difference''' | |||
[[File:8.png]] | [[File:8.png]] | ||
As stated above, the potential difference from one point to another in space is calculated as the line integral of the electric field and the time rate of change of magnetic field along that path (alternate way - multiply electric field times the distance covered across the two points). The voltage between point A to point B is equal to the work which would have to be done, per unit charge, against or by the electric field to move the charge from A to B. The voltage between the two ends of a path is the total energy required to move a small electric charge along that path, divided by the magnitude of the charge. Both an unchanging electric field and a dynamic electromagnetic field must be included in determining the voltage between two points. | |||
Potential difference is defined in such a way that negatively charged objects are pulled towards higher voltages, while positively charged objects are pulled towards lower voltages. This means that the conventional current in a always flows from higher voltage to lower voltage. Current can flow from lower voltage to higher voltage, but only when a source of energy is present to push it against the opposing electric field. For example, inside a battery, chemical reactions provide the energy needed for ion current to flow from the negative to the positive terminal. | |||
Revision as of 20:40, 12 April 2016
Claimed by Daniel Kurniawan
Electric Potential Difference, otherwise known as Voltage, is the difference in electric potential energy between two points per unit of electric charge. The voltage between two points is equal to the work done per unit of charge against a static electric field to move the test charge between two points and is measured in units of volts.
Voltage can be caused by static electric fields, by electric current through a magnetic field, by time-varying magnetic fields, or some combination of these three. One can use a voltmeter to measure the potential difference between two points in a circuit. A voltage may represent either a source of energy (electromotive force), or lost, used, or stored energy (potential drop).
Voltage
Definition
Say you have two points "A" and "B" in space. The potential difference is defined as the difference in electric potential between those two points. Electric potential is electric potential energy per unit charge, measured in joules per coulomb, otherwise known as volts.
Calculating Potential Difference
As stated above, the potential difference from one point to another in space is calculated as the line integral of the electric field and the time rate of change of magnetic field along that path (alternate way - multiply electric field times the distance covered across the two points). The voltage between point A to point B is equal to the work which would have to be done, per unit charge, against or by the electric field to move the charge from A to B. The voltage between the two ends of a path is the total energy required to move a small electric charge along that path, divided by the magnitude of the charge. Both an unchanging electric field and a dynamic electromagnetic field must be included in determining the voltage between two points.
Potential difference is defined in such a way that negatively charged objects are pulled towards higher voltages, while positively charged objects are pulled towards lower voltages. This means that the conventional current in a always flows from higher voltage to lower voltage. Current can flow from lower voltage to higher voltage, but only when a source of energy is present to push it against the opposing electric field. For example, inside a battery, chemical reactions provide the energy needed for ion current to flow from the negative to the positive terminal.