Sinusoidal Electromagnetic Radiaton: Difference between revisions
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Frequency=== | ===Frequency=== | ||
Frequency measures the number of oscillations in a given time. It is therefore the inverse of the period and its unit is either seconds inverse or Hertz. Frequency is also related to angular frequent w in radians per second by f=w/ | Frequency measures the number of oscillations in a given time. It is therefore the inverse of the period and its unit is either seconds inverse or Hertz. Frequency is also related to angular frequent w in radians per second by <br /><math>f=\frac{w}{2pi}</math>. | ||
===Wavelength=== | ===Wavelength=== | ||
Revision as of 13:10, 4 December 2015
Made and claimed by Ida De Vierno
The Main Idea
Being able to mathematically relate the speed, wavelength and period of a sinusoidal electromagnetic wave. Understanding how radiation emitted is affected by a charge moving sinusoidally.
Electromagnetic Radiation
When a charge initially begins accelerating, it will take time before we can observe this change in field. When we are close to the point charge, we can see the field of a moving charge whereas further away we see the field of a stationary charge. Between these two areas, is the stretched field lines in the shell which is what we know as electromagnetic radiation. When a charge experiences momentary acceleration, it emits only a brief pulse of radiation. This differs from when the charge is moved sinusoidally as the charge will emit continuous radiation.
Charge Moving Sinusoidally
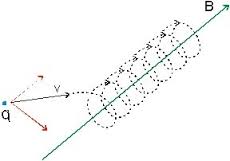
Sinusoidal is a mathematic curve that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation (think the sin curve). Thus a sinusoidal acceleration takes place when the charge is moving in any oscillatory manner. The stretched field lines that were discusses early are thus continuously varying and sinusoidal. Eectromagnetic radiation occurs only at the frequency of oscillation.
When a charge is moved sinusoidally, we can find the position of charge by
[math]\displaystyle{ y=ymax\sin(wt) }[/math]
where [math]\displaystyle{ w }[/math] is the angular frequency in radians per second.
Will the electromagnetic radiation also be be emitted sinusoidally?
Yes. This can be proven by differentiating position to find velocity before differentiating again to find the acceleration. This sinusoidal acceleration is what causes the sinusoidal electromagnetic radiation.
[math]\displaystyle{ v_y=\frac{dy}{dt}=wymax\cos(wt) }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ a_y=\frac{dv_y}{dt}=-w^2ymax\sin(wt) }[/math]
Amplitude
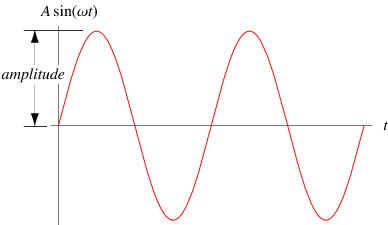
Amplitude is the height of the maximum peak during oscillation. As seen from the diagram, we only measure the distance from the x axis and do not include the area below the axis. The amplitude is also the maximum magnitude of the electric field.
Period
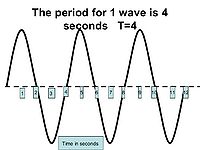
The sinusoidal motion results in waves that continually repeat, much like the sin curve. The period measures the amount of time it takes to complete one repeated cycle. As seen in the diagram, one cycle begins at 1 second and ends at 5 seconds. Thus the period of this graph would be four seconds.
Frequency
Frequency measures the number of oscillations in a given time. It is therefore the inverse of the period and its unit is either seconds inverse or Hertz. Frequency is also related to angular frequent w in radians per second by
[math]\displaystyle{ f=\frac{w}{2pi} }[/math].
Wavelength
Speed
Speed of propagation of electromagnetic wave can be measured in two different ways.
- The first way is by following the maximum amplitude (the peak of the oscillation). You will notice that it travels one wavelength in a period. Thus speed of crest is
- Another way is using the it of the arrival of the radiative electric field.
These two ways of calculating speed will give you a constant answer in a vacuum. However discrepancies can occur in space through which light wave has to travel to water, glass or even air.
Polarized Radiation
Polarization refers to the orientation of electric field, in which it can be aligned only along one axis. Radiation can also be unpolarized as in the case of natural light due to the charges oscillating along different directions.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, according to frequency and wavelength.
A Mathematical Model
What are the mathematical equations that allow us to model this topic. For example [math]\displaystyle{ {\frac{d\vec{p}}{dt}}_{system} = \vec{F}_{net} }[/math] where p is the momentum of the system and F is the net force from the surroundings.
A Computational Model
How do we visualize or predict using this topic. Consider embedding some vpython code here Teach hands-on with GlowScript
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Show that the electromagnetic radiation emitted is sinusoidally when the charge is moving sinusoidally.
Connectedness
Is there an interesting industrial application?
Understanding electromagnetic radiation and being able to calculate wavelength and frequency is needed in the areas of communication such as the television and the radio. Knowing the fundamentals has resulted in the development of technology for sending speech and music through the airwaves.
History
Electromagnetic waves was first discovered in the nineteenth century when an unexpected correlation between electric phenomena and velocity of light was found. James Maxwell who founded the Maxwell equation not only realized that electric field and magnetic field cover together form electromagnetic wave but that changing magnetic field will cause a change in electric field. In 1887, using Maxwell's theories, Heinrich Hertz produced waves and also found methods to detect these ways. Using two rods to serve as receivers and a spark gap to act as the antennae. Every time a wave was picked up, it would create a spark. By doing this, Hertz proved that signals had the properties of electromagnetic waves. The unit for frequency was thus named after him.
See also
Are there related topics or categories in this wiki resource for the curious reader to explore? How does this topic fit into that context?
Further reading
Books, Articles or other print media on this topic
External links
References
This section contains the the references you used while writing this page