Spring Potential Energy: Difference between revisions
Scarswell3 (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
(Added tables to the main idea sections that include common mistakes made when conceptualizing springs, and added a few more examples to the connectedness section) |
||
| (26 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Shlesh Sakpal (Ss87) Fall 2025 11/19/2025''' | |||
This topic covers Spring Potential Energy. | This topic covers Spring Potential Energy. | ||
==The Main Idea== | ==The Main Idea== | ||
[[File:spring2456.png|thumb|500 px| Spring Potential Energy]] | |||
Spring potential energy, also known as elastic potential energy,is the stored energy in a spring, that can potentially be converted into kinetic energy. The energy stored in the spring is due to the deformation of the spring, often from stretching and compressing. The force excreted to stretch or compress a spring is known as Hooke's law, '''F<sub>s</sub> = -k<sub>s</sub>x''', where '''F<sub>s</sub>''' is force, '''x''' is the displacement, and '''-k<sub>s</sub>''' is the spring constant. The spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. If a spring is not stretched or compressed, then it is at equilibrium. At equilibrium a spring has no potential energy, assuming there is no force being applied to the spring. | |||
===A Mathematical Model=== | ===A Mathematical Model=== | ||
The formula for | The formula for Force of a Spring: | ||
'''F<sub>s</sub> = -k<sub>s</sub>x | |||
'''U<sub>s</sub>=<sup>1</sup>⁄<sub>2</sub>k<sub>s</sub> | The formula for Spring Potential Energy: | ||
'''U<sub>s</sub> = <sup>1</sup>⁄<sub>2</sub>k<sub>s</sub>x<sup>2</sup>''' | |||
where: | where: | ||
'''k<sub>s</sub>'''= spring constant | '''k<sub>s</sub>''' = spring constant | ||
''' | '''x<sup>2</sup>''' = stretch measured from the equilibrium point; | ||
===A Computational Model=== | |||
'''An oscillating spring on the floor:''' | |||
=== | GlowScript 2.9 VPython | ||
display(width=600,height=600,center=vector(6,0,0),background=color.black) | |||
mbox=2 | |||
L0 = vector(9,0,0) | |||
ks = 1 | |||
deltat = .01 | |||
t = 0 | |||
wall=box(pos=vector(0,1,0),size=vector(0.2,3,2),color=color.cyan) | |||
floor=box(pos=vector(7.2,-0.6,0),size=vector(14,0.2,4),color=color.cyan) | |||
box=box(pos=vector(12,0,0),size=vector(1,1,1),color=color.red) | |||
pivot=vector(0,0,0) | |||
spring=helix(pos=pivot,axis=box.pos-pivot,radius=0.4,constant=1,thickness=0.1,coils=20,color=color.orange) | |||
box.p = vector(0,0,0) | |||
while (t<50): | |||
rate(100) | |||
s = wall.pos - box.pos | |||
Fspring=(L0-box.pos)*(ks) | |||
box.p= box.p +Fspring*deltat | |||
box.pos = box.pos + box.p*deltat | |||
spring.axis = box.pos - spring.pos | |||
t = t+ deltat | |||
[[File:spring2457.png|500 px| Oscillating Spring on Floor]] | |||
Link to Simulation: | |||
https://trinket.io/glowscript/3146b836dc | |||
'''A hanging oscillating spring:''' | |||
from __future__ import division | |||
from visual import * | |||
from visual.graph import * | |||
scene.width=600 | |||
scene.height = 760 | |||
g = 9.8 | |||
mball = .2 | |||
Lo = 0.3 | |||
ks = 12 | |||
deltat = 1e-3 | |||
t = 0 | |||
ceiling = box(pos=(0,0,0), size = (0.5, 0.01, 0.2)) | |||
ball = sphere(pos=(0,-0.3,0), radius=0.025, color=color.yellow) | |||
spring = helix(pos=ceiling.pos, color=color.green, thickness=.005, coils=10, radius=0.01) | |||
spring.axis = ball.pos - ceiling.pos | |||
vball = vector(0.02,0,0) | |||
ball.p = mball*vball | |||
scene.autoscale = 0 | |||
scene.center = vector(0,-Lo,0) | |||
while t < 10: | |||
rate(1000) | rate(1000) | ||
L_vector = (mag(ball.pos) - Lo)* ball.pos.norm() | L_vector = (mag(ball.pos) - Lo)* ball.pos.norm() | ||
| Line 52: | Line 87: | ||
spring.axis = ball.pos-ceiling.pos | spring.axis = ball.pos-ceiling.pos | ||
t = t + deltat | t = t + deltat | ||
[[File:Animated-mass-spring-faster.gif|200 px]] | |||
'''Code to visualize a spring's motion given x and y coordinate input:''' | |||
Web VPython 3.2 | |||
scene.background = color.white | |||
ball = sphere(radius=0.03, color=color.blue) | |||
trail = curve(color=ball.color) | |||
origin = sphere(pos=vector(0,0,0), color=color.yellow, radius=0.015) | |||
spring = helix(color=color.cyan, thickness=0.006, coils=40, radius=0.015) | |||
spring.pos = origin.pos | |||
xplot = graph(title="x-position vs time", xtitle="time (s)", ytitle="x-position (m)") | |||
xposcurve = gcurve(color=color.blue, width=4, label="model") | |||
xpos2curve = gcurve(color=color.red, width=4, label="experiment") | |||
yplot = graph(title="y-position vs time", xtitle="time (s)", ytitle="y-position (m)") | |||
yposcurve = gcurve(color=color.blue, width=4, label="model") | |||
ypos2curve = gcurve(color=color.red, width=4, label="experiment") | |||
eplot = graph(title="Change in Energy vs Time", xtitle="Time (s)", ytitle="Change in Energy (J)") | |||
dKcurve = gcurve(color=color.blue, width=4, label="deltaK") | |||
dUgcurve = gcurve(color=color.red, width=4, label="deltaUgrav") | |||
dUscurve = gcurve(color=color.green, width=4, label="deltaUspring") | |||
dEcurve = gcurve(color=color.orange, width=4, label="deltaE") | |||
ball2 = sphere(radius=0.025, color=color.red) | |||
ball.m = 0.402 | |||
ball.pos = vector(0.55,-0.0039,0) | |||
ball.vel = vector(0,0,0) | |||
X = [] | |||
Y = [] | |||
obs = read_local_file(scene.title_anchor).text; | |||
for line in obs.split('\n'): | |||
if line != '': | |||
line = line.split(',') | |||
X.append(float(line[0])) | |||
Y.append(float(line[1])) | |||
idx = 0 #variable used to select data from list. | |||
cnt = 0 #variable to keep track of predictions made between each measurement | |||
t = 0 | |||
deltat = (5.5/len(X))/20 #choose this small AND an integer multiple of the time interval between frames of experiment video | |||
g = 9.8 | |||
k_s = 8.87 | |||
L0 = 0.123 | |||
L = spring.pos-ball.pos | |||
Lhat = L/mag(L) | |||
s = mag(L)-L0 | |||
K = (1/2)*ball.m*mag(ball.vel)**2 # kinetic energy | |||
Ug = ball.m * g * ball.pos.y # gravitational potential energy | |||
Us = 1/2*k_s*s**2 # spring potential energy | |||
E = K + Ug + Us # total energy | |||
while t < 5.5: | |||
K_i = K | |||
Ug_i = Ug | |||
Us_i = Us | |||
E_i = E | |||
Fgrav = vector(0,-ball.m*g,0) | |||
Fspring = -k_s*s*Lhat | |||
Fnet = Fspring + Fgrav | |||
ball.vel = ball.vel+(Fnet/ball.m)*deltat | |||
ball.pos = ball.pos+ball.vel*deltat | |||
L = ball.pos-spring.pos | |||
Lhat = L/mag(L) | |||
s = mag(L)-L0 | |||
spring.axis = L | |||
trail.append(pos=ball.pos) | |||
K = (1/2)*ball.m*mag(ball.vel)**2 | |||
deltaK = K-K_i | |||
Ug = ball.m*g*ball.pos.y | |||
deltaUg = Ug-Ug_i | |||
Us = 1/2*k_s*s**2 | |||
deltaUs = Us-Us_i | |||
E = K + Ug + Us | |||
deltaE = deltaK+deltaUg+deltaUs | |||
dKcurve.plot(t,deltaK) # blue | |||
dUgcurve.plot(t,deltaUg) # red | |||
dUscurve.plot(t,deltaUs) # green | |||
dEcurve.plot(t,deltaE) # orange | |||
xposcurve.plot(t,ball.pos.x) | |||
yposcurve.plot(t,ball.pos.y) | |||
# Update time | |||
t = t + deltat | |||
rate(1000) | |||
===Common Mistakes and Misconceptions with Spring Problems=== | |||
Students usually struggle with signs and displacement when working with Hooke's Law. Here are some common misconceptions that are made when working with springs. | |||
{| class = "wikitable" | |||
! Misconception | |||
! Why It's Wrong | |||
! Correct Idea | |||
|- | |||
| The sign in Hooke's Law doesn't matter | |||
| The negative sign in Hooke's Law is often dropped students | |||
| The negative sign shows that the force always points toward equilibrium | |||
|- | |||
| x is the total length of the spring | |||
| Students often plug in L instead of <math>(L - L_0)</math> | |||
| x must be the displacement from equilibrium, not the total length | |||
|- | |||
| Springs store energy only when stretched | |||
| Students often forget that compression also stores energy | |||
| Spring potential energy depends on **any** displacement from equilibrium | |||
|- | |||
| Spring potential energy is negative when the spring is compressed | |||
| Students confuse spring energy with gravitational potential energy | |||
| Spring potential energy is always positive because it depends on x² | |||
|} | |||
===Spring Quantities at a Glance=== | |||
{| class = "wikitable" | |||
! Quantity | |||
! Symbol | |||
! Formula | |||
! Units | |||
! Meaning | |||
|- | |||
| Spring force | |||
| <math>F_s</math> | |||
| <math>F_s = -kx</math> | |||
| N | |||
| Restoring force toward equilibrium. | |||
|- | |||
| Spring potential energy | |||
| <math>U_s</math> | |||
| <math>U_s = \frac{1}{2}kx^2</math> | |||
| J | |||
| Stored elastic energy. | |||
|- | |||
| Stretch/compression | |||
| <math>x</math> | |||
| <math>x = L - L_0</math> | |||
| m | |||
| Displacement from equilibrium. | |||
|- | |||
| Spring constant | |||
| <math>k</math> | |||
| — | |||
| N/m | |||
| Measures stiffness of the spring. | |||
|} | |||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| Line 59: | Line 237: | ||
===Simple=== | ===Simple=== | ||
'''Question''' | |||
If a spring's spring constant is 200 N/m and it is stretched 1.5 meters from rest, what is the potential spring energy? | If a spring's spring constant is 200 N/m and it is stretched 1.5 meters from rest, what is the potential spring energy? | ||
'''Solution''' | |||
'''k<sub>s'''= 200 N/m | '''k<sub>s'''= 200 N/m | ||
| Line 65: | Line 248: | ||
'''s'''= 1.5 m | '''s'''= 1.5 m | ||
'''U<sub>s'''=(0.5)k<sub> | '''U<sub>s'''=(0.5)k<sub>s</sub>s<sup>2 | ||
'''U<sub>s'''= (0.5)(200 N/m)(1.5 m)<sup>2 | '''U<sub>s'''= (0.5)(200 N/m)(1.5 m)<sup>2 | ||
| Line 72: | Line 255: | ||
===Middling=== | ===Middling=== | ||
'''Question''' | |||
A horizontal spring with stiffness 0.6 N/m has a relaxed length of 10 cm. A mass of 25 g is attached and you stretch the spring to a length of 20 cm. The mass is released and moves with little friction. What is the speed of the mass at the moment when the spring returns to its relaxed length of 10cm? | A horizontal spring with stiffness 0.6 N/m has a relaxed length of 10 cm. A mass of 25 g is attached and you stretch the spring to a length of 20 cm. The mass is released and moves with little friction. What is the speed of the mass at the moment when the spring returns to its relaxed length of 10cm? | ||
'''Solution''' | |||
'''k<sub>s'''= 0.6 N/m | '''k<sub>s'''= 0.6 N/m | ||
| Line 78: | Line 266: | ||
'''s'''= 0.1 m | '''s'''= 0.1 m | ||
'''U<sub>s'''=(.5)k<sub> | '''U<sub>s'''=(.5)k<sub>s</sub>s<sup>2</sup> = (.5)(0.6 N/m)(0.1 m)<sup>2 | ||
'''U<sub>s'''= 0.003 J | '''U<sub>s''' = 0.003 J | ||
Potential Energy is Converted into Kinetic Energy (K): | Potential Energy is Converted into Kinetic Energy (K): | ||
'''U<sub>s'''= K | '''U<sub>s''' = K | ||
'''U<sub>s'''=(0.5)mv<sup>2 | '''U<sub>s''' =(0.5)mv<sup>2 | ||
0.003 J=(0.5)(0.025 kg)v<sup>2 | 0.003 J = (0.5)(0.025 kg)v<sup>2 | ||
'''v<sup>2'''=<sup>(0.003 J)</sup>⁄<sub>((0.5)(0.025 kg)</sub> | '''v<sup>2''' = <sup>(0.003 J)</sup>⁄<sub>((0.5)(0.025 kg))</sub> | ||
'''v<sup>2'''=0.24 J/kg*s | '''v<sup>2''' = 0.24 J/kg*s | ||
'''v''' = 0.49 m/s | |||
===Difficult=== | ===Difficult=== | ||
'''Question''' | |||
A package of mass 9 kg sits on an airless asteroid with mass 8.0x10<sup>20</sup> kg and radius 8.7x10<sup>5</sup> m. Your goal is to launch the package so that it will never come back and when it is very far away it will have a speed of 226 m/s. You have a spring whose stiffness is 2.8x10<sup>5</sup> N/m. How much must you compress the spring? | A package of mass 9 kg sits on an airless asteroid with mass 8.0x10<sup>20</sup> kg and radius 8.7x10<sup>5</sup> m. Your goal is to launch the package so that it will never come back and when it is very far away it will have a speed of 226 m/s. You have a spring whose stiffness is 2.8x10<sup>5</sup> N/m. How much must you compress the spring? | ||
'''Solution''' | |||
The initial condition for escape from the asteroid is: | The initial condition for escape from the asteroid is: | ||
| Line 114: | Line 307: | ||
'''s'''=2.36 m | '''s'''=2.36 m | ||
===Graphing=== | |||
'''Energy graph''' | |||
The energy graph of a oscillating spring continuously switches between kinetic and potential energy because springs are continuously returning to equilibrium. The following is an example of a computational model of a hanging spring with an initial force in the positive x direction. As seen below, the energies the spring contains will always equal out to zero despite each fluctuating individually. | |||
[[File:Spring energy.jpg]] | |||
==Connectedness== | ==Connectedness== | ||
Because springs are all around us, from Slinkies to parts in automobiles, spring potential energy is useful in everyday life. One example of this is a trampoline. Without potential spring energy to allow for bounce, a trampoline would simply be a boring stretch of fabric. Spring potential is also used to absorb shock in vehicles. This allows for a smoother ride while traveling over bumps in the road. | Because springs are all around us, from Slinkies to parts in automobiles, spring potential energy is useful in everyday life. One example of this is a trampoline. Without potential spring energy to allow for bounce, a trampoline would simply be a boring stretch of fabric. Spring potential is also used to absorb shock in vehicles. This allows for a smoother ride while traveling over bumps in the road. An extreme example of spring energy we commonly come across is the mechanism for garage doors. These doors contain large springs that allow them to open and close. These springs can lift an average of 400 pounds, giving them a huge amount of potential energy. | ||
===Some Real World Applications of Spring Potential Energy=== | |||
Examples of springs being used can be found all over our daily lives, even in places you wouldn't expect. For example, they are found in: | |||
* Car Suspension Systems | |||
* Mechanical Watches | |||
* Trampolines | |||
* Archery | |||
* Exercise Equipment | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Device | |||
! Type of “Spring” | |||
! What the Energy Becomes | |||
|- | |||
| Car suspension | |||
| Metal coil + damper | |||
| Mostly heat due to damping. | |||
|- | |||
| Trampoline | |||
| Metal springs and elastic fabric | |||
| Kinetic and gravitational potential energy when being used. | |||
|- | |||
| Archery | |||
| Elastic bow (not a metal spring) | |||
| Kinetic energy of the arrow. | |||
|- | |||
| Mechanical watches | |||
| The mainspring winds up and slowly releases spring potential energy to turn the watch | |||
| Mechanical motion of gears. | |||
|} | |||
[[File:trampoline.jpg|thumb|Trampoline Potential Energy]] | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| Line 126: | Line 360: | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Spring potential energy is | Spring potential energy is related to [[Hooke's Law]] and [[Potential Energy]]. | ||
===Further reading=== | ===Further reading=== | ||
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/pespr.html | |||
https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-physics-1/ap-work-and-energy/spring-potential-energy-and-hookes-law-ap/a/spring-force-and-energy-ap1 | |||
https://openstax.org/books/university-physics-volume-1/pages/8-1-potential-energy-of-a-system | |||
===External links=== | ===External links=== | ||
[http:// | [http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/energy/Lesson-1/Potential-Energy] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
#http://www.universetoday.com/55027/hookes-law/ | #http://www.universetoday.com/55027/hookes-law/ | ||
#http://www.scienceclarified.com/everyday/Real-Life-Physics-Vol-2/Oscillation-Real-life-applications.html | #http://www.scienceclarified.com/everyday/Real-Life-Physics-Vol-2/Oscillation-Real-life-applications.html | ||
#http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/pespr.html | |||
#Chabay and Bruce A. Sherwood. Matter & Interactions. 4th ed. | #Chabay and Bruce A. Sherwood. Matter & Interactions. 4th ed. | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Energy]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:27, 19 November 2025
Shlesh Sakpal (Ss87) Fall 2025 11/19/2025
This topic covers Spring Potential Energy.
The Main Idea
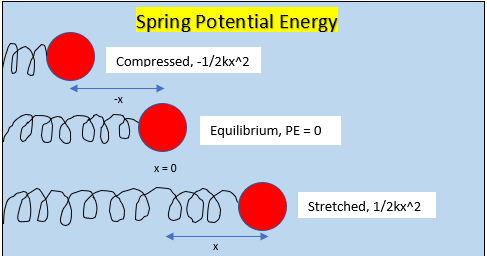
Spring potential energy, also known as elastic potential energy,is the stored energy in a spring, that can potentially be converted into kinetic energy. The energy stored in the spring is due to the deformation of the spring, often from stretching and compressing. The force excreted to stretch or compress a spring is known as Hooke's law, Fs = -ksx, where Fs is force, x is the displacement, and -ks is the spring constant. The spring constant being unique for every spring depends on factors such as material and thickness of coiled wire. If a spring is not stretched or compressed, then it is at equilibrium. At equilibrium a spring has no potential energy, assuming there is no force being applied to the spring.
A Mathematical Model
The formula for Force of a Spring:
Fs = -ksx
The formula for Spring Potential Energy:
Us = 1⁄2ksx2
where:
ks = spring constant
x2 = stretch measured from the equilibrium point;
A Computational Model
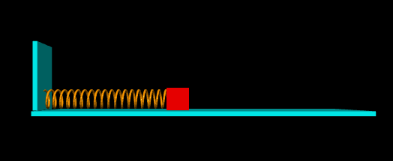
An oscillating spring on the floor:
GlowScript 2.9 VPython display(width=600,height=600,center=vector(6,0,0),background=color.black) mbox=2 L0 = vector(9,0,0) ks = 1 deltat = .01 t = 0 wall=box(pos=vector(0,1,0),size=vector(0.2,3,2),color=color.cyan) floor=box(pos=vector(7.2,-0.6,0),size=vector(14,0.2,4),color=color.cyan) box=box(pos=vector(12,0,0),size=vector(1,1,1),color=color.red) pivot=vector(0,0,0) spring=helix(pos=pivot,axis=box.pos-pivot,radius=0.4,constant=1,thickness=0.1,coils=20,color=color.orange) box.p = vector(0,0,0) while (t<50): rate(100) s = wall.pos - box.pos Fspring=(L0-box.pos)*(ks) box.p= box.p +Fspring*deltat box.pos = box.pos + box.p*deltat spring.axis = box.pos - spring.pos t = t+ deltat
Link to Simulation: https://trinket.io/glowscript/3146b836dc
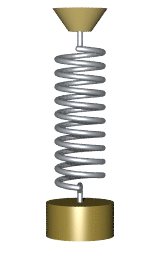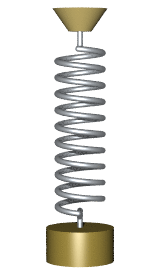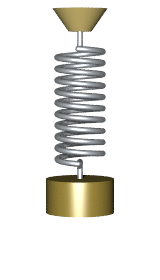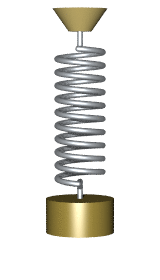
A hanging oscillating spring:
from __future__ import division from visual import * from visual.graph import * scene.width=600 scene.height = 760 g = 9.8 mball = .2 Lo = 0.3 ks = 12 deltat = 1e-3 t = 0 ceiling = box(pos=(0,0,0), size = (0.5, 0.01, 0.2)) ball = sphere(pos=(0,-0.3,0), radius=0.025, color=color.yellow) spring = helix(pos=ceiling.pos, color=color.green, thickness=.005, coils=10, radius=0.01) spring.axis = ball.pos - ceiling.pos vball = vector(0.02,0,0) ball.p = mball*vball scene.autoscale = 0 scene.center = vector(0,-Lo,0) while t < 10: rate(1000) L_vector = (mag(ball.pos) - Lo)* ball.pos.norm() Fspring = -ks * L_vector Fgrav = vector(0,-mball * g,0) Fnet = Fspring + Fgrav ball.p = ball.p + Fnet * deltat ball.pos = ball.pos + (ball.p/mball) * deltat spring.axis = ball.pos-ceiling.pos t = t + deltat
Code to visualize a spring's motion given x and y coordinate input:
Web VPython 3.2 scene.background = color.white ball = sphere(radius=0.03, color=color.blue) trail = curve(color=ball.color) origin = sphere(pos=vector(0,0,0), color=color.yellow, radius=0.015) spring = helix(color=color.cyan, thickness=0.006, coils=40, radius=0.015) spring.pos = origin.pos xplot = graph(title="x-position vs time", xtitle="time (s)", ytitle="x-position (m)") xposcurve = gcurve(color=color.blue, width=4, label="model") xpos2curve = gcurve(color=color.red, width=4, label="experiment") yplot = graph(title="y-position vs time", xtitle="time (s)", ytitle="y-position (m)") yposcurve = gcurve(color=color.blue, width=4, label="model") ypos2curve = gcurve(color=color.red, width=4, label="experiment") eplot = graph(title="Change in Energy vs Time", xtitle="Time (s)", ytitle="Change in Energy (J)") dKcurve = gcurve(color=color.blue, width=4, label="deltaK") dUgcurve = gcurve(color=color.red, width=4, label="deltaUgrav") dUscurve = gcurve(color=color.green, width=4, label="deltaUspring") dEcurve = gcurve(color=color.orange, width=4, label="deltaE") ball2 = sphere(radius=0.025, color=color.red) ball.m = 0.402 ball.pos = vector(0.55,-0.0039,0) ball.vel = vector(0,0,0) X = [] Y = [] obs = read_local_file(scene.title_anchor).text; for line in obs.split('\n'):
if line != :
line = line.split(',')
X.append(float(line[0]))
Y.append(float(line[1]))
idx = 0 #variable used to select data from list. cnt = 0 #variable to keep track of predictions made between each measurement t = 0 deltat = (5.5/len(X))/20 #choose this small AND an integer multiple of the time interval between frames of experiment video g = 9.8 k_s = 8.87 L0 = 0.123 L = spring.pos-ball.pos Lhat = L/mag(L) s = mag(L)-L0 K = (1/2)*ball.m*mag(ball.vel)**2 # kinetic energy Ug = ball.m * g * ball.pos.y # gravitational potential energy Us = 1/2*k_s*s**2 # spring potential energy E = K + Ug + Us # total energy while t < 5.5:
K_i = K Ug_i = Ug Us_i = Us E_i = E Fgrav = vector(0,-ball.m*g,0) Fspring = -k_s*s*Lhat Fnet = Fspring + Fgrav ball.vel = ball.vel+(Fnet/ball.m)*deltat ball.pos = ball.pos+ball.vel*deltat L = ball.pos-spring.pos Lhat = L/mag(L) s = mag(L)-L0 spring.axis = L trail.append(pos=ball.pos) K = (1/2)*ball.m*mag(ball.vel)**2 deltaK = K-K_i Ug = ball.m*g*ball.pos.y deltaUg = Ug-Ug_i Us = 1/2*k_s*s**2 deltaUs = Us-Us_i E = K + Ug + Us deltaE = deltaK+deltaUg+deltaUs dKcurve.plot(t,deltaK) # blue dUgcurve.plot(t,deltaUg) # red dUscurve.plot(t,deltaUs) # green dEcurve.plot(t,deltaE) # orange xposcurve.plot(t,ball.pos.x) yposcurve.plot(t,ball.pos.y) # Update time t = t + deltat rate(1000)
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions with Spring Problems
Students usually struggle with signs and displacement when working with Hooke's Law. Here are some common misconceptions that are made when working with springs.
| Misconception | Why It's Wrong | Correct Idea |
|---|---|---|
| The sign in Hooke's Law doesn't matter | The negative sign in Hooke's Law is often dropped students | The negative sign shows that the force always points toward equilibrium |
| x is the total length of the spring | Students often plug in L instead of [math]\displaystyle{ (L - L_0) }[/math] | x must be the displacement from equilibrium, not the total length |
| Springs store energy only when stretched | Students often forget that compression also stores energy | Spring potential energy depends on **any** displacement from equilibrium |
| Spring potential energy is negative when the spring is compressed | Students confuse spring energy with gravitational potential energy | Spring potential energy is always positive because it depends on x² |
Spring Quantities at a Glance
| Quantity | Symbol | Formula | Units | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring force | [math]\displaystyle{ F_s }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ F_s = -kx }[/math] | N | Restoring force toward equilibrium. |
| Spring potential energy | [math]\displaystyle{ U_s }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ U_s = \frac{1}{2}kx^2 }[/math] | J | Stored elastic energy. |
| Stretch/compression | [math]\displaystyle{ x }[/math] | [math]\displaystyle{ x = L - L_0 }[/math] | m | Displacement from equilibrium. |
| Spring constant | [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math] | — | N/m | Measures stiffness of the spring. |
Examples
Be sure to show all steps in your solution and include diagrams whenever possible
Simple
Question
If a spring's spring constant is 200 N/m and it is stretched 1.5 meters from rest, what is the potential spring energy?
Solution
ks= 200 N/m
s= 1.5 m
Us=(0.5)kss2
Us= (0.5)(200 N/m)(1.5 m)2
Us= 225 J
Middling
Question
A horizontal spring with stiffness 0.6 N/m has a relaxed length of 10 cm. A mass of 25 g is attached and you stretch the spring to a length of 20 cm. The mass is released and moves with little friction. What is the speed of the mass at the moment when the spring returns to its relaxed length of 10cm?
Solution
ks= 0.6 N/m
s= 0.1 m
Us=(.5)kss2 = (.5)(0.6 N/m)(0.1 m)2
Us = 0.003 J
Potential Energy is Converted into Kinetic Energy (K):
Us = K
Us =(0.5)mv2
0.003 J = (0.5)(0.025 kg)v2
v2 = (0.003 J)⁄((0.5)(0.025 kg))
v2 = 0.24 J/kg*s
v = 0.49 m/s
Difficult
Question
A package of mass 9 kg sits on an airless asteroid with mass 8.0x1020 kg and radius 8.7x105 m. Your goal is to launch the package so that it will never come back and when it is very far away it will have a speed of 226 m/s. You have a spring whose stiffness is 2.8x105 N/m. How much must you compress the spring?
Solution
The initial condition for escape from the asteroid is:
Ki+Ui=1⁄2mvesc2 + (-G*Mm⁄R)=0
Potential energy of the spring equals the total energy in the system.
1⁄2kss2=1⁄2mvesc2 +(-G*Mm⁄R)
s2= m⁄ks(2GM⁄R +v2)=s2 = 9⁄2.8x105(2G8.0x1020⁄8.7x105+2262)
s2=5.58 m
s=2.36 m
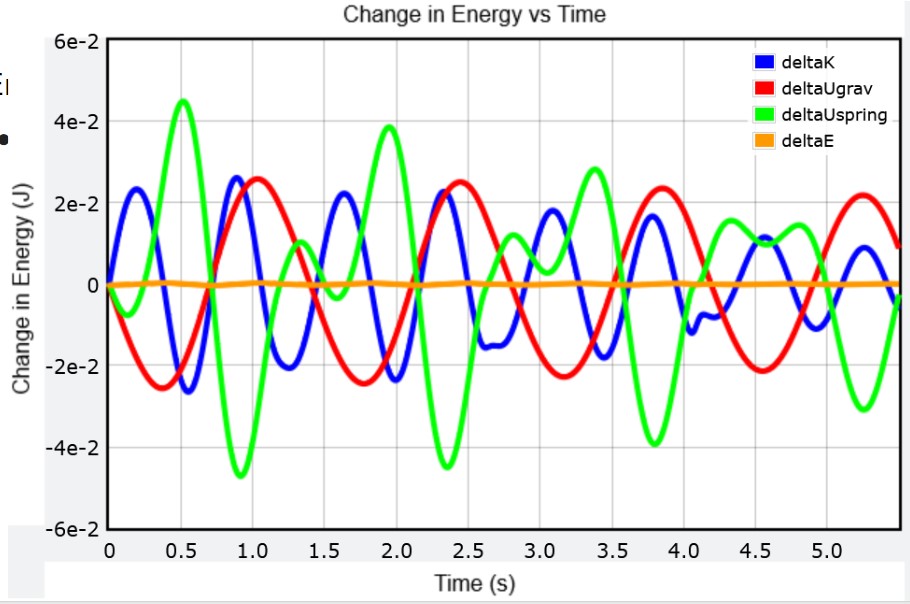
Graphing
Energy graph
The energy graph of a oscillating spring continuously switches between kinetic and potential energy because springs are continuously returning to equilibrium. The following is an example of a computational model of a hanging spring with an initial force in the positive x direction. As seen below, the energies the spring contains will always equal out to zero despite each fluctuating individually.
Connectedness
Because springs are all around us, from Slinkies to parts in automobiles, spring potential energy is useful in everyday life. One example of this is a trampoline. Without potential spring energy to allow for bounce, a trampoline would simply be a boring stretch of fabric. Spring potential is also used to absorb shock in vehicles. This allows for a smoother ride while traveling over bumps in the road. An extreme example of spring energy we commonly come across is the mechanism for garage doors. These doors contain large springs that allow them to open and close. These springs can lift an average of 400 pounds, giving them a huge amount of potential energy.
Some Real World Applications of Spring Potential Energy
Examples of springs being used can be found all over our daily lives, even in places you wouldn't expect. For example, they are found in:
- Car Suspension Systems
- Mechanical Watches
- Trampolines
- Archery
- Exercise Equipment
| Device | Type of “Spring” | What the Energy Becomes |
|---|---|---|
| Car suspension | Metal coil + damper | Mostly heat due to damping. |
| Trampoline | Metal springs and elastic fabric | Kinetic and gravitational potential energy when being used. |
| Archery | Elastic bow (not a metal spring) | Kinetic energy of the arrow. |
| Mechanical watches | The mainspring winds up and slowly releases spring potential energy to turn the watch | Mechanical motion of gears. |

History
Elastic Potential Energy stemmed from the ideas of Robert Hooke, a 17th century British physicist who studied the relationship between forces applied to springs and elasticity. Hooke’s Law, which is a principle that states that the that the force needed to extend or compress a spring by a distance is proportional to that distance.
See also
Spring potential energy is related to Hooke's Law and Potential Energy.
Further reading
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/pespr.html
https://openstax.org/books/university-physics-volume-1/pages/8-1-potential-energy-of-a-system
External links
References
- http://www.universetoday.com/55027/hookes-law/
- http://www.scienceclarified.com/everyday/Real-Life-Physics-Vol-2/Oscillation-Real-life-applications.html
- http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/pespr.html
- Chabay and Bruce A. Sherwood. Matter & Interactions. 4th ed.