Tension: Difference between revisions
Chloejhkim (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
(→Simple) |
||
| (120 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Main Idea== | |||
[[File:tension1.png | right | 200px]] [[File:tension2.png| right | 200px]] | |||
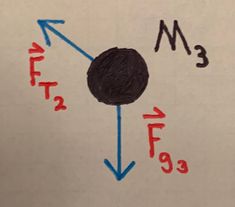
Tension is the force exerted by a rope (or anything that can be used to hang another object) on the object that is hanging from it. Usually, ropes and cables create a tension force. In general, anything that is flexible can pull an object and create a tension force. In consequence, the tension force can only be a pulling force. The rope will eventually go slack if someone tries to push with a rope, and it will act like an object. Later we will see that this concept will help with draing force diagrams with the force of tension always pulling the object. | |||
Tension is considered a contact force which means that the force is exerted when objects are touching. Usually, the force of tension is the force that is transmitted through a rope. If someone is pulling on a block with a rope, the person exerting force on the rope which transmits that force to the block. In problems, the ropes and cables will usually be massless, which perfectly transfers the force. | |||
===Mathematical Model=== | |||
There is no fundamental equation to calculate a tension force (<math>F_T</math>). Instead, one must usually deduce what the tension force must be based on the other forces acting on the object. To do this, Newton's Second and Third Laws will be very important. | |||
We start by stating Newton's Second Law (the next force on a mass <math>M</math> is equal to the sum of the forces acting on the mass): | |||
:<math>F_{net} = \sum F = Ma</math> | |||
The force of tension will end up being one of the forces in the sum. Furthermore, since the tension force usually acts between two objects (pulling each other in opposite directions), we usually get a system of equations (such as in a pulley system with two masses connected by a rope) that can be used to solve for the force of tension. | |||
The | |||
The examples will go in further detail. | |||
===Computational Model=== | |||
In this code, a mass in the shape of a ball is hung from a 10 meter string, raised to an initial position, and then let go. With the loop, we follow the ball's pendulum-like motion. | |||
[[File:TGifCModel.gif|400px|right]] | |||
<code> | |||
from __future__ import division | |||
from visual import * | |||
from visual.graph import * | |||
</code> | |||
SCENE: | |||
<code> | |||
https://www. | |||
scene.title = "Mass on a String" | |||
scene.background = color.black | |||
</code> | |||
CONSTANTS: | |||
<code> | |||
L = 10 #Length of string in meters | |||
g = vector(0, -9.8, 0) #Acceleration due to gravity | |||
mass = 5 #Mass of the ball in kilograms | |||
</code> | |||
OBJECTS: | |||
<code> | |||
ceiling = box(pos = vector(0, 0, 0), size = vector(20, 1, 1), color = color.red) | |||
ball = sphere(pos = vector(10 * cos(-20 * (pi/180) ), 10 * sin(-20 * (pi/180)), 0), radius = 1, color = color.cyan) | |||
string = curve(pos = [ceiling.pos, ball.pos], radius = .1, color = color.yellow) | |||
trail = curve(pos = [ball.pos]) | |||
</code> | |||
TIME: | |||
<code> | |||
time = 0 #Time in seconds | |||
dtime = .001 #Time step for each iteration | |||
</code> | |||
ANGLE: | |||
<code> | |||
theta = - 20 * (pi / 180) #Angle to the vertical in radians #Left of the vertical is a negative angle #Right of the vertical is a positive angle #(-20) - (-160) | |||
</code> | |||
INITIAL CONDITIONS: | |||
<code> | |||
ball.p = vector(0,0,0) #Initial momentum of the block is 0 | |||
initpos = vector(-10 / 2**(1/2), -10 / 2**(1/2), 0) | |||
</code> | |||
CALCULATIONS: | |||
<code> | |||
Fgravity = mass * g #A vector | |||
Ftension = vector(0,0,0) | |||
</code> | |||
LOOP: | |||
<code> | |||
while time < 10 and theta > -160 * (pi/180): | |||
rate(500) | |||
Ftension.y = -Fgravity.y | |||
magFtension = - Ftension.y / sin(theta) #Positive always | |||
Ftension.x = - magFtension * cos(theta) #Negative until theta < -90 | |||
#Updates: | |||
ball.p.x += Ftension.x * dtime | |||
ball.pos.x += (ball.p.x * dtime) / mass | |||
if ball.pos.x >= 10: | |||
print(time) | |||
break | |||
ball.pos.y = -(100 - (ball.pos.x)**2)**(1/2) | |||
time += dtime | |||
theta = arctan(ball.pos.y/ball.pos.x) | |||
string.pos = [ceiling.pos, ball.pos] | |||
trail.append(ball.pos) | |||
</code> | |||
==Examples== | |||
The three examples will be helpful in cementing an understanding of the concept of tension, and they will get harder as we go. | |||
===Simple=== | |||
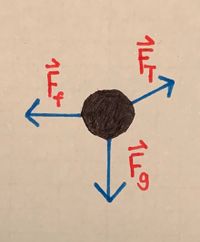
[[File:TSimpleSketch.jpeg| 400px|right|thumb|A diagram for the simple example]] | |||
A <math>2 \ \text{kg}</math> toy box is being dragged by a child. To do so, the child is pulling on a rope that is tied to the toy box. This rope makes an angle of <math>\theta = 60^\text{o}</math> with the horizontal. There is a frictional force between the box and the floor with a coefficient of kinetic friction <math>\mu_k = 0.2</math>. With the x-axis as the horizontal shown in the image, and the y-axis as the vertical shown in the image, the toy box gains an acceleration of: | |||
:<math>\mathbf{a} = \begin{bmatrix} a_x \\ a_y \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 3 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} \frac{m}{s^2}</math> | |||
:'''a) Calculate the tension force''' <math>F_T</math> '''that is present in the child's rope:''' | |||
::First, we start by drawing a free body diagram for the toy box. The main forces acting on the box are the gravitational force, normal force, frictional force, and tension force. | |||
::[[File:TSimpleFBD.jpeg|200px]] | |||
::Now, we will write down the forces acting on the box: | |||
:::<math>F_g = mg = 2 \times 9.81 = 19.62 \ \text{Newtons}</math> | |||
:::<math>F_N = \ ?</math><br> | |||
::::We know the normal force is not equal to the gravitational force because part of the tension accelerates the box upwards | |||
:::<math>F_f = \mu_k F_N = \ ?</math><br> | |||
::::We need to find the normal force to find this | |||
:::<math>F_T = \ ?</math><br> | |||
::::This is what we are looking to solve for | |||
::Next, we use Newton's Laws (mainly the second) to sum the forces along the x-axis and the y-axis and set them equal to their respective accelerations: | |||
:::<math>F_{net_x} = \sum F_x = ma_{net_x} = F_T \ \text{cos}(\theta) - F_f = F_T \ \text{cos}(\theta) - \mu_k F_N = 2 \times 3 = 6 \ \text{Newtons}</math> '''(1)''' | |||
:::<math>F_{net_y} = \sum F_y = ma_{net_y} = F_T \ \text{sin}(\theta) + F_N - F_g = F_T \ \text{sin}(\theta) + F_N - mg = 0 \ \text{Newtons}</math> '''(2)''' | |||
::We have two equations (1 and 2) and two unknowns (<math>F_N \ \text{and} \ F_T</math>). Therefore, we have a good chance at solving for these two forces with our equations 1 and 2. We will add these two equations together to get: | |||
:::<math>F_{net_x} + F_{net_y} = m(a_{net_x} + a_{net_y}) = F_T(cos(\theta) + sin(\theta)) + F_N(1 - \mu_k) - F_g = 6</math> | |||
::Therefore: | |||
:::<math>F_T = \frac{6 + F_g - F_N(1 - \mu_k)}{\text{cos}(\theta) + \text{sin}(\theta)}</math> '''(3)''' | |||
::Using our equation for <math>F_{net_x}</math> and plugging in the expression (3) for <math>F_T</math>, we get: | |||
:::<math>F_{net_x} = ma_{net_x} = \left( \frac{6 + F_g - F_N(1 - \mu_k)}{\text{cos}(\theta) + \text{sin}(\theta)} \right) \text{cos}(\theta) - \mu_k F_N = 6</math> | |||
::This simplifies to: | |||
:::<math>\left(\frac{6 + 19.62 - 0.8F_N}{\text{cos}(60^\text{o}) + \text{sin}(60^\text{o})}\right) \times 0.5 - 0.2F_N = 6</math> | |||
::This equals: | |||
:::<math>(18.7551 - 0.5856F_N) \times 0.5 - 0.2 F_N = 6</math> | |||
::With further more simplification, this equals: | |||
:::<math>9.3776 - 0.2928F_N - 0.2F_N = 6</math> | |||
::Leading to <math>F_N</math> being equal to: | |||
:::<math>F_N = 6.9 \ \text{Newtons}</math> | |||
::Now, using this value of <math>F_N</math>, we can calculate <math>F_T</math> from our previous expression for it (3): | |||
:::<math>F_T = \frac{6 + 19.62 -0.8F_N}{1.366} = \frac{25.62 - 0.8 \times 6.9}{1.366} = 14.7 \ \text{Newtons}</math> | |||
::In vector form: | |||
:::<math>\mathbf{F_T} = \begin{bmatrix} F_T \ \text{cos}(\theta) \\ F_T \ \text{sin}(\theta) \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 7.35 \\ 12.73 \end{bmatrix} \ \text{Newtons}</math> | |||
===Middling=== | |||
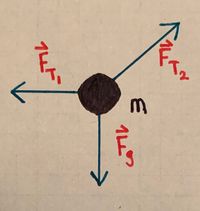
[[File:TMiddlingSketch.jpeg|300px|right|thumb|A diagram for the middling example]] | |||
A box with mass <math>m</math> hangs in a static state from two ropes. One rope is attached to the ceiling with an angle <math>\theta = 30^\text{o}</math> to the horizontal. The other rope, which pulls the box to the left, is along the horizontal (to the left of the box) and attached to a wall. Refer to the diagram for any confusion. | |||
:'''a) What is the tension in the rope attached to the wall''' (<math>F_{T_1}</math>) '''and the rope attached to the ceiling''' (<math>F_{T_2}</math>)?''' | |||
::First, as always, we should draw a free body diagram: | |||
::[[File:TMiddlingFBD.jpeg|200px]] | |||
::Referring to the free body diagram, we see the main forces acting on the box are: | |||
:::<math>F_g = mg</math> | |||
:::<math>F_{T_1} = \ ?</math><br> | |||
::::We are solving for this | |||
:::<math>F_{T_2} = \ ?</math><br> | |||
::::We are solving for this | |||
::Note that the acceleration of the box (<math>\mathbf{a_{net}}</math>) is <math>\mathbf{0}</math>.<br> | |||
::Using Newton's Laws and this note, we see that the sums of the forces along the x and y axes are as follows: | |||
:::<math>F_{net_x} = F_{T_{2_x}} - F_{T_{1_x}} = F_{T_2} \ \text{cos}(\theta) - F_{T_1} \ \text{cos}(0^\text{o}) = F_{T_2} \ \text{cos}(30^\text{o}) - F_{T_1} = 0</math> | |||
::::'''Therefore:''' | |||
:::::<math>F_{T_1} = F_{T_2} \ \text{cos}(30^\text{o})</math> '''(1)''' | |||
:::<math>F_{net_y} = F_{T_{2_y}} + F_{T_{1_y}} - F_g = F_{T_2} \ \text{sin}(\theta) + F_{T_1} \ \text{sin}(0^\text{0}) - F_g = F_{T_2} \ \text{sin}(30^\text{o}) - F_g = 0</math> | |||
::::'''Therefore:''' | |||
:::::<math>F_{T_2} = \frac{F_g}{\text{sin}(30^\text{o})}</math> '''(2)''' | |||
::Using these two relations (1 and 2), we can say that: | |||
:::<math>F_{T_1} = \frac{F_g}{\text{sin}(\theta)} \ \text{cos}(\theta) = \frac{mg \ \text{cos}(\theta)}{\text{sin}(\theta)} = 1.73mg</math> | |||
:::<math>F_{T_2} = \frac{F_g}{\text{sin}(\theta)} = \frac{mg}{\text{sin}(\theta)} = 2mg</math> | |||
::In vector form: | |||
:::<math>F_{T_1} = \begin{bmatrix} 1.73mg \ \text{cos}(180^\text{o}) \\ 1.73mg \ \text{sin}(180^\text{o}) \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} - 1.73 mg \\ 0 \end{bmatrix}</math> | |||
:::<math>F_{T_2} = \begin{bmatrix} 2mg \ \text{cos}(30^\text{o}) \\ 2mg \ \text{sin}(30^\text{o}) \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1.73 mg \\ mg \end{bmatrix}</math> | |||
===Difficult=== | |||
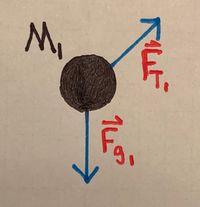
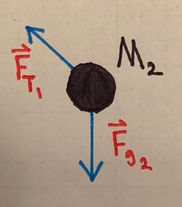
[[File:TDifficultSketch.jpeg|400px|right|thumb|A diagram of the difficult example]] | |||
A block of mass <math>M_1</math> (block 1) is positioned on a ramp that is in the shape of an inclined plane. The angle between the horizontal and the inclined plane is <math>\theta = 45^\text{o}</math>. Block 1 has a string of negligible mass attached to it. This string loops over a pulley, and then connects to a block of mass <math>M_2</math> (block 2), which is sitting on another inclined plane, whose angle to the horizontal is <math>\phi = 20^\text{o}</math>. Block 2 has another string of negligible mass attached to its opposite side. This string connects to another block of mass <math>M_3</math> (block 3), who is on the same inclined plane as block 2. All strings are held tightly between the blocks. | |||
:'''a) What is the acceleration of the system''' (<math>a_{system}</math>) '''of blocks (blocks 1, 2, and 3):''' | |||
::We will start by drawing a free body diagram for each block: | |||
::[[File:TDifficultFBD1.jpeg|200px]] [[File:TDifficultFBD2.jpeg|182px]] [[File:TDifficultFBD3.jpeg|235px]] | |||
::Note that since all the strings are held tight, all the blocks will have the same acceleration along the axis perpendicular to inclined planes (<math>a_x</math>) | |||
::Now, for each block we will use Newton's Second Law to find an expression for the net force along the axis parallel to the inclined planes: | |||
:::Block 1: | |||
::::<math>F_{net_{x_1}} = F_{T_1} - F_{g_1} \text{sin}(\theta) = M_1 a_{net_x}</math> | |||
:::Block 2: | |||
::::<math>F_{net_{x_2}} = F_{T_2} + F_{g_2} \text{sin}(\phi) - F_{T_1} = M_2 a_{net_x}</math> | |||
:::Block 3: | |||
::::<math>F_{net_{x_3}} = F_{g_3} \text{sin}(\phi) - F_{T_2} = M_3 a_{net_x}</math> | |||
::Adding these three equations together leads to: | |||
:::<math>F_{net_{x_1}} + F_{net_{x_2}} + F_{net_{x_3}} = (F_{T_1} - F_{T_1}) + (F_{T_2} - F_{T_2}) + (F_{g_2} + F_{g_3}) \text{sin}(\phi) - F_{g_1} \text{sin}(\theta) = (M_1 + M_2 + M_3) a_{net_x}</math> | |||
::Simplifying gives: | |||
:::<math>(M_1 + M_2 + M_3)a_{net_x} = (F_{g_2} + F_{g_3}) \text{sin}(\phi) - F_{g_1} \text{sin}(\theta)</math> | |||
::Therefore: | |||
:::<math>a_{net_x} = \frac{\left((M_2 + M_3)\text{sin}(\phi) - M_1 \text{sin}(\theta)\right)g}{M_1 + M_2 + M_3}</math> | |||
::We know the acceleration along the perpendicular direction to the inclined planes is <math>0</math> since the blocks will not be moving away from or into the planes. | |||
::Therefore the acceleration of the system is: | |||
:::<math>a_{system} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\left((M_2 + M_3)\text{sin}(\phi) - M_1 \text{sin}(\theta)\right)g}{M_1 + M_2 + M_3} \\ 0 \end{bmatrix}</math> | |||
==Connectedness== | |||
Force of tension is used a lot in the real world, from small everyday things, such as yoyo's to large construction projections. In everyday life, force of tension can be seen when someone is trying to hang anything from somewhere else by a string. Tension can be very useful in construction as well because it can help support beams or other large objects. The rope has to be strong enough or else if there is too much force of tension, the rope could snap and drop whatever it is suppose to hold up. | |||
One typical application of the force of tension is in elevators. If you look at a clear elevator, you can see all the ropes that hope the elevator up. The whole elevator system is acting as a pulley and pulling a rope up and letting it go down. The force of tension must be very meticulously calculated so that the rope is strong enough for a lot of people in the elevator. You can notice that most elevators will show what the maximum weight is, and that is calculated by seeing how much force of tension the ropes connected to the elevator can take and converting that to a maximum weight that it can hold. If there is too much weight in the elevator, it may break and the elevator will fall down the shaft. | |||
==History== | |||
Tension forces have been in use for centuries. Any system, for example a wooden pulley system one may have seen in a 1600's theatre, with a taut wire, cable, string, chain, etcetera uses the force of tension. Its wide use is no accident. Being able to attach a strong tension carrying material (like a chain)l to a heavy object, makes the lifting and moving of the object much easier. For example, no skyscraper is built without the use of large cranes. At the heart of a crane, a strong cable is looped around the heavy object, and then the crane can lift, rotate, and move an object that would be nearly impossible for us alone. In this way, most skyscrapers are built. It is speculated that the ancient Egyptians used a combination of inclined planes and strong ropes to build the pyramids. | |||
We can see that the tension force has always been a very important part of construction, giving it a long history. | |||
==See also== | |||
===Further Reading=== | |||
:Chabay, Ruth W., and Bruce A. Sherwood. Matter & Interactions. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. Print. | |||
:[[Free Body Diagram]]<br> | |||
:[[Inclined Plane]]<br> | |||
:[[Compression or Normal Force]]<br> | |||
:[[Newton's Second Law: the Momentum Principle]]<br> | |||
:[[Net Force]]<br> | |||
:[[Gravitational Force Near Earth]]<br> | |||
:[[Weight]]<br> | |||
:[[VPython]] | |||
===External Links=== | |||
:http://philschatz.com/physics-book/contents/m42075.html https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/forces-newtons-laws/tension-tutorial/a/what-is-tension | |||
==References== | |||
:Chabay, Ruth W., and Bruce A. Sherwood. Matter & Interactions. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. Print. https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/forces-newtons-laws/tension-tutorial/a/what-is-tension | |||
:http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/newtlaws/U2L2b.cfm#tension http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/mlif.html http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/elev.html http://www.sparknotes.com/physics/dynamics/newtonapplications/problems_2.html | |||
:http://philschatz.com/physics-book/contents/m42075.html http://www.mrwaynesclass.com/freebodies/reading/pics/Tension_Explained_Diagram.png http://www.softschools.com/formulas/physics/tension_formula/70/ | |||
:http://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/36175/understanding-tension http://www.brightstorm.com/science/physics/newtons-laws-of-motion/tension/ | |||
Latest revision as of 14:37, 19 October 2019
Main Idea
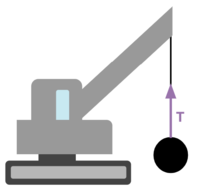
Tension is the force exerted by a rope (or anything that can be used to hang another object) on the object that is hanging from it. Usually, ropes and cables create a tension force. In general, anything that is flexible can pull an object and create a tension force. In consequence, the tension force can only be a pulling force. The rope will eventually go slack if someone tries to push with a rope, and it will act like an object. Later we will see that this concept will help with draing force diagrams with the force of tension always pulling the object.
Tension is considered a contact force which means that the force is exerted when objects are touching. Usually, the force of tension is the force that is transmitted through a rope. If someone is pulling on a block with a rope, the person exerting force on the rope which transmits that force to the block. In problems, the ropes and cables will usually be massless, which perfectly transfers the force.
Mathematical Model
There is no fundamental equation to calculate a tension force ([math]\displaystyle{ F_T }[/math]). Instead, one must usually deduce what the tension force must be based on the other forces acting on the object. To do this, Newton's Second and Third Laws will be very important.
We start by stating Newton's Second Law (the next force on a mass [math]\displaystyle{ M }[/math] is equal to the sum of the forces acting on the mass):
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net} = \sum F = Ma }[/math]
The force of tension will end up being one of the forces in the sum. Furthermore, since the tension force usually acts between two objects (pulling each other in opposite directions), we usually get a system of equations (such as in a pulley system with two masses connected by a rope) that can be used to solve for the force of tension.
The examples will go in further detail.
Computational Model
In this code, a mass in the shape of a ball is hung from a 10 meter string, raised to an initial position, and then let go. With the loop, we follow the ball's pendulum-like motion.
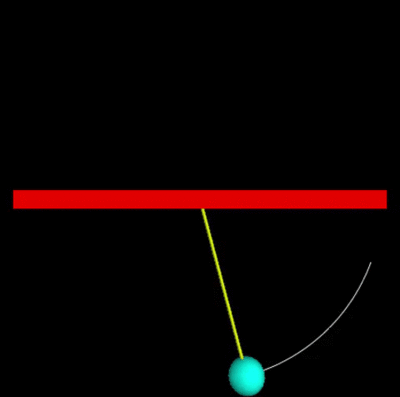
from __future__ import division
from visual import *
from visual.graph import *
SCENE:
scene.title = "Mass on a String"
scene.background = color.black
CONSTANTS:
L = 10 #Length of string in meters
g = vector(0, -9.8, 0) #Acceleration due to gravity
mass = 5 #Mass of the ball in kilograms
OBJECTS:
ceiling = box(pos = vector(0, 0, 0), size = vector(20, 1, 1), color = color.red)
ball = sphere(pos = vector(10 * cos(-20 * (pi/180) ), 10 * sin(-20 * (pi/180)), 0), radius = 1, color = color.cyan)
string = curve(pos = [ceiling.pos, ball.pos], radius = .1, color = color.yellow)
trail = curve(pos = [ball.pos])
TIME:
time = 0 #Time in seconds
dtime = .001 #Time step for each iteration
ANGLE:
theta = - 20 * (pi / 180) #Angle to the vertical in radians #Left of the vertical is a negative angle #Right of the vertical is a positive angle #(-20) - (-160)
INITIAL CONDITIONS:
ball.p = vector(0,0,0) #Initial momentum of the block is 0
initpos = vector(-10 / 2**(1/2), -10 / 2**(1/2), 0)
CALCULATIONS:
Fgravity = mass * g #A vector
Ftension = vector(0,0,0)
LOOP:
while time < 10 and theta > -160 * (pi/180):
rate(500)
Ftension.y = -Fgravity.y
magFtension = - Ftension.y / sin(theta) #Positive always
Ftension.x = - magFtension * cos(theta) #Negative until theta < -90
#Updates:
ball.p.x += Ftension.x * dtime
ball.pos.x += (ball.p.x * dtime) / mass
if ball.pos.x >= 10:
print(time)
break
ball.pos.y = -(100 - (ball.pos.x)**2)**(1/2)
time += dtime
theta = arctan(ball.pos.y/ball.pos.x)
string.pos = [ceiling.pos, ball.pos]
trail.append(ball.pos)
Examples
The three examples will be helpful in cementing an understanding of the concept of tension, and they will get harder as we go.
Simple
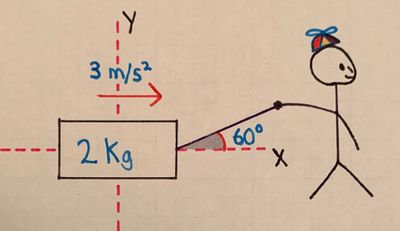
A [math]\displaystyle{ 2 \ \text{kg} }[/math] toy box is being dragged by a child. To do so, the child is pulling on a rope that is tied to the toy box. This rope makes an angle of [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = 60^\text{o} }[/math] with the horizontal. There is a frictional force between the box and the floor with a coefficient of kinetic friction [math]\displaystyle{ \mu_k = 0.2 }[/math]. With the x-axis as the horizontal shown in the image, and the y-axis as the vertical shown in the image, the toy box gains an acceleration of:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{a} = \begin{bmatrix} a_x \\ a_y \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 3 \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} \frac{m}{s^2} }[/math]
- a) Calculate the tension force [math]\displaystyle{ F_T }[/math] that is present in the child's rope:
- First, we start by drawing a free body diagram for the toy box. The main forces acting on the box are the gravitational force, normal force, frictional force, and tension force.
- Now, we will write down the forces acting on the box:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_g = mg = 2 \times 9.81 = 19.62 \ \text{Newtons} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_N = \ ? }[/math]
- We know the normal force is not equal to the gravitational force because part of the tension accelerates the box upwards
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_N = \ ? }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_f = \mu_k F_N = \ ? }[/math]
- We need to find the normal force to find this
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_f = \mu_k F_N = \ ? }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_T = \ ? }[/math]
- This is what we are looking to solve for
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_T = \ ? }[/math]
- Next, we use Newton's Laws (mainly the second) to sum the forces along the x-axis and the y-axis and set them equal to their respective accelerations:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_x} = \sum F_x = ma_{net_x} = F_T \ \text{cos}(\theta) - F_f = F_T \ \text{cos}(\theta) - \mu_k F_N = 2 \times 3 = 6 \ \text{Newtons} }[/math] (1)
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_y} = \sum F_y = ma_{net_y} = F_T \ \text{sin}(\theta) + F_N - F_g = F_T \ \text{sin}(\theta) + F_N - mg = 0 \ \text{Newtons} }[/math] (2)
- We have two equations (1 and 2) and two unknowns ([math]\displaystyle{ F_N \ \text{and} \ F_T }[/math]). Therefore, we have a good chance at solving for these two forces with our equations 1 and 2. We will add these two equations together to get:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_x} + F_{net_y} = m(a_{net_x} + a_{net_y}) = F_T(cos(\theta) + sin(\theta)) + F_N(1 - \mu_k) - F_g = 6 }[/math]
- Therefore:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_T = \frac{6 + F_g - F_N(1 - \mu_k)}{\text{cos}(\theta) + \text{sin}(\theta)} }[/math] (3)
- Using our equation for [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_x} }[/math] and plugging in the expression (3) for [math]\displaystyle{ F_T }[/math], we get:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_x} = ma_{net_x} = \left( \frac{6 + F_g - F_N(1 - \mu_k)}{\text{cos}(\theta) + \text{sin}(\theta)} \right) \text{cos}(\theta) - \mu_k F_N = 6 }[/math]
- This simplifies to:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \left(\frac{6 + 19.62 - 0.8F_N}{\text{cos}(60^\text{o}) + \text{sin}(60^\text{o})}\right) \times 0.5 - 0.2F_N = 6 }[/math]
- This equals:
- [math]\displaystyle{ (18.7551 - 0.5856F_N) \times 0.5 - 0.2 F_N = 6 }[/math]
- With further more simplification, this equals:
- [math]\displaystyle{ 9.3776 - 0.2928F_N - 0.2F_N = 6 }[/math]
- Leading to [math]\displaystyle{ F_N }[/math] being equal to:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_N = 6.9 \ \text{Newtons} }[/math]
- Now, using this value of [math]\displaystyle{ F_N }[/math], we can calculate [math]\displaystyle{ F_T }[/math] from our previous expression for it (3):
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_T = \frac{6 + 19.62 -0.8F_N}{1.366} = \frac{25.62 - 0.8 \times 6.9}{1.366} = 14.7 \ \text{Newtons} }[/math]
- In vector form:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{F_T} = \begin{bmatrix} F_T \ \text{cos}(\theta) \\ F_T \ \text{sin}(\theta) \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 7.35 \\ 12.73 \end{bmatrix} \ \text{Newtons} }[/math]
Middling
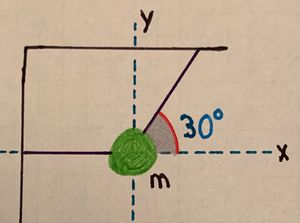
A box with mass [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math] hangs in a static state from two ropes. One rope is attached to the ceiling with an angle [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = 30^\text{o} }[/math] to the horizontal. The other rope, which pulls the box to the left, is along the horizontal (to the left of the box) and attached to a wall. Refer to the diagram for any confusion.
- a) What is the tension in the rope attached to the wall ([math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_1} }[/math]) and the rope attached to the ceiling ([math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_2} }[/math])?
- First, as always, we should draw a free body diagram:
- Referring to the free body diagram, we see the main forces acting on the box are:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_g = mg }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_1} = \ ? }[/math]
- We are solving for this
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_1} = \ ? }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_2} = \ ? }[/math]
- We are solving for this
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_2} = \ ? }[/math]
- Note that the acceleration of the box ([math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{a_{net}} }[/math]) is [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{0} }[/math].
- Using Newton's Laws and this note, we see that the sums of the forces along the x and y axes are as follows:
- Note that the acceleration of the box ([math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{a_{net}} }[/math]) is [math]\displaystyle{ \mathbf{0} }[/math].
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_x} = F_{T_{2_x}} - F_{T_{1_x}} = F_{T_2} \ \text{cos}(\theta) - F_{T_1} \ \text{cos}(0^\text{o}) = F_{T_2} \ \text{cos}(30^\text{o}) - F_{T_1} = 0 }[/math]
- Therefore:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_1} = F_{T_2} \ \text{cos}(30^\text{o}) }[/math] (1)
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_y} = F_{T_{2_y}} + F_{T_{1_y}} - F_g = F_{T_2} \ \text{sin}(\theta) + F_{T_1} \ \text{sin}(0^\text{0}) - F_g = F_{T_2} \ \text{sin}(30^\text{o}) - F_g = 0 }[/math]
- Therefore:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_2} = \frac{F_g}{\text{sin}(30^\text{o})} }[/math] (2)
- Using these two relations (1 and 2), we can say that:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_1} = \frac{F_g}{\text{sin}(\theta)} \ \text{cos}(\theta) = \frac{mg \ \text{cos}(\theta)}{\text{sin}(\theta)} = 1.73mg }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_2} = \frac{F_g}{\text{sin}(\theta)} = \frac{mg}{\text{sin}(\theta)} = 2mg }[/math]
- In vector form:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_1} = \begin{bmatrix} 1.73mg \ \text{cos}(180^\text{o}) \\ 1.73mg \ \text{sin}(180^\text{o}) \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} - 1.73 mg \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{T_2} = \begin{bmatrix} 2mg \ \text{cos}(30^\text{o}) \\ 2mg \ \text{sin}(30^\text{o}) \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1.73 mg \\ mg \end{bmatrix} }[/math]
Difficult
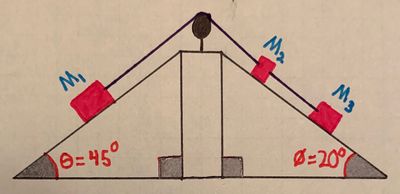
A block of mass [math]\displaystyle{ M_1 }[/math] (block 1) is positioned on a ramp that is in the shape of an inclined plane. The angle between the horizontal and the inclined plane is [math]\displaystyle{ \theta = 45^\text{o} }[/math]. Block 1 has a string of negligible mass attached to it. This string loops over a pulley, and then connects to a block of mass [math]\displaystyle{ M_2 }[/math] (block 2), which is sitting on another inclined plane, whose angle to the horizontal is [math]\displaystyle{ \phi = 20^\text{o} }[/math]. Block 2 has another string of negligible mass attached to its opposite side. This string connects to another block of mass [math]\displaystyle{ M_3 }[/math] (block 3), who is on the same inclined plane as block 2. All strings are held tightly between the blocks.
- a) What is the acceleration of the system ([math]\displaystyle{ a_{system} }[/math]) of blocks (blocks 1, 2, and 3):
- We will start by drawing a free body diagram for each block:
- Note that since all the strings are held tight, all the blocks will have the same acceleration along the axis perpendicular to inclined planes ([math]\displaystyle{ a_x }[/math])
- Now, for each block we will use Newton's Second Law to find an expression for the net force along the axis parallel to the inclined planes:
- Block 1:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_{x_1}} = F_{T_1} - F_{g_1} \text{sin}(\theta) = M_1 a_{net_x} }[/math]
- Block 2:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_{x_2}} = F_{T_2} + F_{g_2} \text{sin}(\phi) - F_{T_1} = M_2 a_{net_x} }[/math]
- Block 3:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_{x_3}} = F_{g_3} \text{sin}(\phi) - F_{T_2} = M_3 a_{net_x} }[/math]
- Adding these three equations together leads to:
- [math]\displaystyle{ F_{net_{x_1}} + F_{net_{x_2}} + F_{net_{x_3}} = (F_{T_1} - F_{T_1}) + (F_{T_2} - F_{T_2}) + (F_{g_2} + F_{g_3}) \text{sin}(\phi) - F_{g_1} \text{sin}(\theta) = (M_1 + M_2 + M_3) a_{net_x} }[/math]
- Simplifying gives:
- [math]\displaystyle{ (M_1 + M_2 + M_3)a_{net_x} = (F_{g_2} + F_{g_3}) \text{sin}(\phi) - F_{g_1} \text{sin}(\theta) }[/math]
- Therefore:
- [math]\displaystyle{ a_{net_x} = \frac{\left((M_2 + M_3)\text{sin}(\phi) - M_1 \text{sin}(\theta)\right)g}{M_1 + M_2 + M_3} }[/math]
- We know the acceleration along the perpendicular direction to the inclined planes is [math]\displaystyle{ 0 }[/math] since the blocks will not be moving away from or into the planes.
- Therefore the acceleration of the system is:
- [math]\displaystyle{ a_{system} = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\left((M_2 + M_3)\text{sin}(\phi) - M_1 \text{sin}(\theta)\right)g}{M_1 + M_2 + M_3} \\ 0 \end{bmatrix} }[/math]
Connectedness
Force of tension is used a lot in the real world, from small everyday things, such as yoyo's to large construction projections. In everyday life, force of tension can be seen when someone is trying to hang anything from somewhere else by a string. Tension can be very useful in construction as well because it can help support beams or other large objects. The rope has to be strong enough or else if there is too much force of tension, the rope could snap and drop whatever it is suppose to hold up.
One typical application of the force of tension is in elevators. If you look at a clear elevator, you can see all the ropes that hope the elevator up. The whole elevator system is acting as a pulley and pulling a rope up and letting it go down. The force of tension must be very meticulously calculated so that the rope is strong enough for a lot of people in the elevator. You can notice that most elevators will show what the maximum weight is, and that is calculated by seeing how much force of tension the ropes connected to the elevator can take and converting that to a maximum weight that it can hold. If there is too much weight in the elevator, it may break and the elevator will fall down the shaft.
History
Tension forces have been in use for centuries. Any system, for example a wooden pulley system one may have seen in a 1600's theatre, with a taut wire, cable, string, chain, etcetera uses the force of tension. Its wide use is no accident. Being able to attach a strong tension carrying material (like a chain)l to a heavy object, makes the lifting and moving of the object much easier. For example, no skyscraper is built without the use of large cranes. At the heart of a crane, a strong cable is looped around the heavy object, and then the crane can lift, rotate, and move an object that would be nearly impossible for us alone. In this way, most skyscrapers are built. It is speculated that the ancient Egyptians used a combination of inclined planes and strong ropes to build the pyramids.
We can see that the tension force has always been a very important part of construction, giving it a long history.
See also
Further Reading
- Chabay, Ruth W., and Bruce A. Sherwood. Matter & Interactions. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. Print.
- Free Body Diagram
- Inclined Plane
- Compression or Normal Force
- Newton's Second Law: the Momentum Principle
- Net Force
- Gravitational Force Near Earth
- Weight
- VPython
External Links
- http://philschatz.com/physics-book/contents/m42075.html https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/forces-newtons-laws/tension-tutorial/a/what-is-tension
References
- Chabay, Ruth W., and Bruce A. Sherwood. Matter & Interactions. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. Print. https://www.khanacademy.org/science/physics/forces-newtons-laws/tension-tutorial/a/what-is-tension
- http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Class/newtlaws/U2L2b.cfm#tension http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/mlif.html http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/elev.html http://www.sparknotes.com/physics/dynamics/newtonapplications/problems_2.html